Task 1: make something that uses only one sensor on Arduino and makes the ellipse in p5 move on the horizontal axis, in the middle of the screen, and nothing on arduino is controlled by p5.
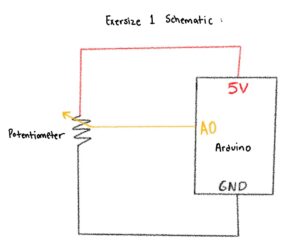
Asma built a simple circuit using an Arduino and a 10kΩ potentiometer to control an on-screen ellipse in p5.js. She connected the potentiometer’s outer legs to 5V and GND and the middle leg to the analog pin A0, allowing it to act as a variable voltage divider. After uploading the Arduino code and checking the serial monitor, she could see how turning the knob changed the analog readings from 0 to 1023. This helped her understand how analog sensors translate physical movement into numerical data that can be visualized digitally.
Arduino code:
const int potPin = A0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int val = analogRead(potPin); // 0..1023
Serial.println(val);
delay(10);
}
P5.js codę:
// === Arduino + p5.js WebSerial (directional movement, fixed) ===
// Pot controls direction/speed by how its value changes. p5 does NOT control Arduino.
let port;
let reader;
let connectButton;
let isConnected = false;
let latestData = null; // last parsed int from serial (0..1023)
let prevData = null; // previous sample to compute delta
let lineBuffer = ''; // accumulate serial chunks until '\n'
let posX = 0; // ellipse position
let speed = 0; // horizontal velocity
function setup() {
createCanvas(windowWidth, windowHeight);
background(240);
textFont('monospace');
connectButton = createButton('Connect to Arduino');
connectButton.position(20, 20);
connectButton.mousePressed(connectToSerial);
// start centered; we'll keep it centered until first data arrives
posX = width / 2;
}
async function connectToSerial() {
try {
// Request and open port
port = await navigator.serial.requestPort();
await port.open({ baudRate: 9600 });
isConnected = true;
console.log(' Port opened');
// Create a text decoder stream and reader for clean line-by-line reads
const textDecoder = new TextDecoderStream();
const readableClosed = port.readable.pipeTo(textDecoder.writable);
reader = textDecoder.readable.getReader();
// Kick off read loop
readSerialLines();
} catch (err) {
console.error(' Connection failed:', err);
isConnected = false;
}
}
async function readSerialLines() {
try {
while (true) {
const { value, done } = await reader.read();
if (done) break; // reader released
if (!value) continue;
// Accumulate and split by newline
lineBuffer += value;
let lines = lineBuffer.split(/\r?\n/);
lineBuffer = lines.pop(); // save incomplete tail
for (let line of lines) {
line = line.trim();
if (!line) continue;
const v = parseInt(line, 10);
if (!Number.isNaN(v)) {
// Clamp to expected 10-bit range
latestData = Math.min(Math.max(v, 0), 1023);
// Initialize prevData on first valid sample
if (prevData === null) prevData = latestData;
}
}
}
} catch (err) {
console.error(' Read error:', err);
} finally {
try { reader && reader.releaseLock(); } catch {}
}
}
function draw() {
background(240);
if (!isConnected) {
fill(200, 0, 0);
noStroke();
textAlign(CENTER, CENTER);
textSize(20);
text("Click 'Connect to Arduino' to begin", width / 2, height / 2);
return;
}
// If we haven't received any valid data yet, show waiting status
if (latestData === null || prevData === null) {
fill(0);
textSize(16);
textAlign(LEFT, TOP);
text('Waiting for data...', 20, 60);
// Keep ellipse centered until first data arrives
} else {
// Change in pot reading determines direction and speed bump
const delta = latestData - prevData;
// Deadband to ignore small noise
const deadband = 4;
if (delta > deadband) {
speed = constrain(speed + 0.6, -12, 12); // turn right -> move right
} else if (delta < -deadband) {
speed = constrain(speed - 0.6, -12, 12); // turn left -> move left
} else {
// friction when knob still
speed *= 0.90;
}
// Integrate position and clamp
posX += speed;
posX = constrain(posX, 0, width);
// Update prev for next frame
prevData = latestData;
}
// Draw ellipse at vertical center
noStroke();
fill(50, 100, 255);
ellipse(posX, height / 2, 80, 80);
// HUD
fill(0);
textSize(14);
textAlign(LEFT, TOP);
const shown = latestData === null ? '—' : latestData;
text( Sensor: ${shown} , 20, 60);
text( Speed: ${nf(speed, 1, 2)} , 20, 80);
}
function windowResized() {
resizeCanvas(windowWidth, windowHeight);
// Keep position on-screen if you resize smaller
posX = constrain(posX, 0, width);
}
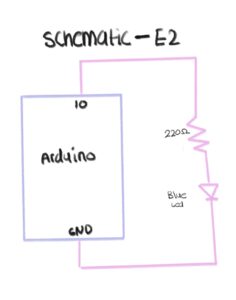
Schematic:
Task 2: make something that controls the LED brightness from p5
Hajar created a simple schematic and circuit using one LED and one resistor connected to the Arduino. Since the main goal was to control the LED’s brightness through serial communication with p5.js, she kept the hardware minimal and focused more on the coding. She first tested the LED with a basic Arduino sketch to make sure everything worked, then created the schematic. Although the circuit was simple and familiar, it still showed her how even a basic setup can become interactive when combined with p5.js.
Arduino code:
const int ledPin = 10; // LED connected to pin 10
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // must match p5.js baud rate
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
int brightness = Serial.read(); // read 0–255
brightness = constrain(brightness, 0, 255);
analogWrite(ledPin, brightness); // control LED brightness
}
}
P5.js codę:
Sketch:
Task 3: take the gravity wind example and make it so every time the ball bounces one led lights up and then turns off, and you can control the wind from one analog sensor
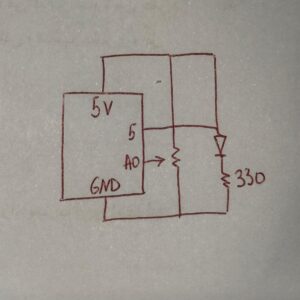
For this project, I combined both physical computing and digital simulation by connecting an Arduino circuit to a p5.js sketch. My setup included a potentiometer to control the wind force in the animation and an LED that lit up every time the falling ball hit the ground. I built a simple circuit using one LED, a resistor, and a 10kΩ potentiometer, and then connected it to my computer through serial communication. Even though the hardware was straightforward, the real challenge came from getting the Arduino and p5.js to communicate properly. I spent a lot of time testing the potentiometer readings, debugging the serial connection, and making sure the LED responded at the right moment in the animation.
P5.js code:
let velocity;
let gravity;
let position;
let acceleration;
let drag = 0.99;
let mass = 50;
let brightnessValue = 0; // Potentiometer value from Arduino (0–5)
let ballDropped = false;
let ledOn = false;
function setup() {
createCanvas(640, 360);
noFill();
textSize(18);
position = createVector(width / 2, 0);
velocity = createVector(0, 0);
acceleration = createVector(0, 0);
gravity = createVector(0, 0.5 * mass);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
fill(0);
if (!ballDropped) {
text("Press D to drop the ball", 20, 30);
text("Press Space Bar to select Serial Port", 20, 50);
return;
}
if (serialActive) {
text("Connected", 20, 30);
text(`Potentiometer: ${brightnessValue}`, 20, 50);
} else {
text("Serial Port Not Connected", 20, 30);
}
// Gravity only (no wind)
applyForce(gravity);
// Update ball
velocity.add(acceleration);
velocity.mult(drag);
position.add(velocity);
acceleration.mult(0);
// Draw ball
ellipse(position.x, position.y, mass, mass);
// Bounce
if (position.y >= height - mass / 2) {
velocity.y *= -0.9;
position.y = height - mass / 2;
// Tell Arduino: turn LED on briefly
if (serialActive && !ledOn) {
writeSerial("1,0\n");
ledOn = true;
}
} else if (ledOn) {
// Tell Arduino: turn LED off
writeSerial("0,0\n");
ledOn = false;
}
}
function applyForce(force) {
let f = p5.Vector.div(force, mass);
acceleration.add(f);
}
// Serial setup and drop ball
function keyPressed() {
if (key == " ") setUpSerial();
if (key == "D" || key == "d") dropBall();
}
function dropBall() {
position.set(width / 2, 0);
velocity.set(0, 0);
mass = 50;
gravity = createVector(0, 0.5 * mass);
ballDropped = true;
}
// Read data from Arduino
function readSerial(data) {
if (data != null) {
let fromArduino = split(trim(data), ",");
if (fromArduino.length === 1) {
brightnessValue = int(fromArduino[0]); // Potentiometer value
}
}
}
Arduino code:
int potPin = A5;
int ledPin = 3;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
analogWrite(ledPin, 255);
delay(200);
analogWrite(ledPin, 0);
}
void loop() {
int raw = analogRead(potPin);
int brightness = map(raw, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
Serial.println(brightness);
// Check for serial commands from p5
if (Serial.available()) {
String data = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
if (data == "1,0") {
analogWrite(ledPin, brightness); // flash with pot brightness
delay(100);
analogWrite(ledPin, 0); // turn off after flash
}
}
delay(30);
}
Sketch:
Video: