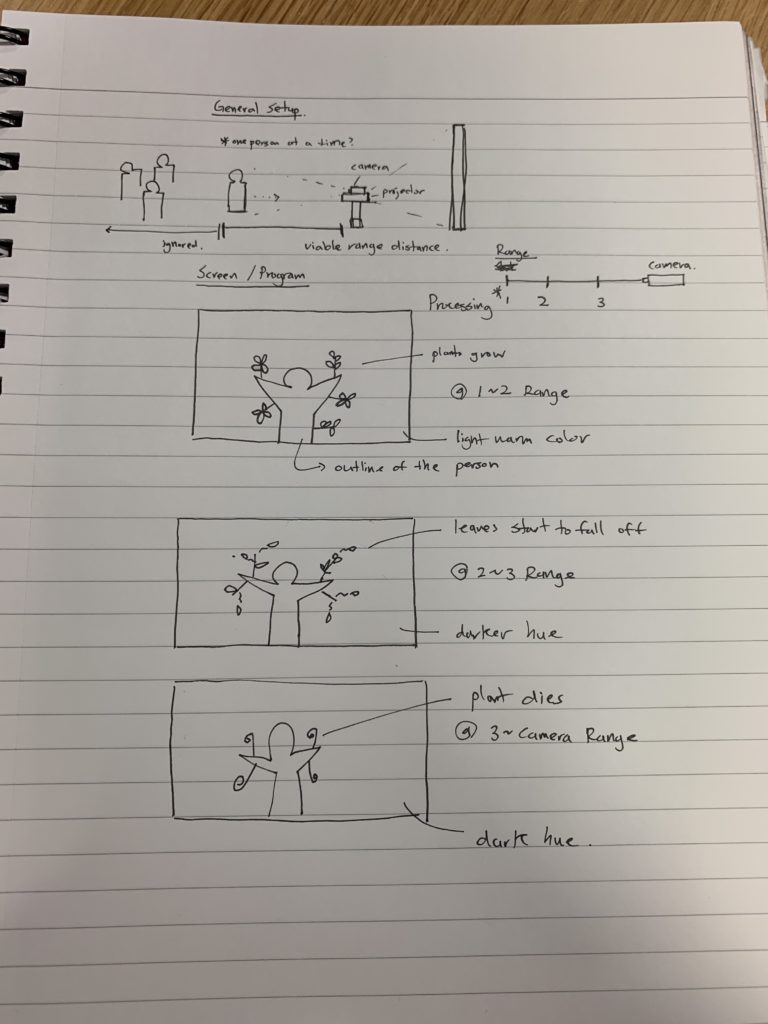
I have always been fascinated with using nature as a medium for interaction and a source for new creation, especially in the area of music.
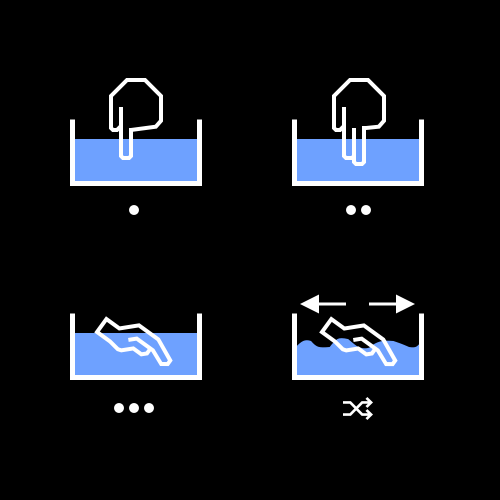
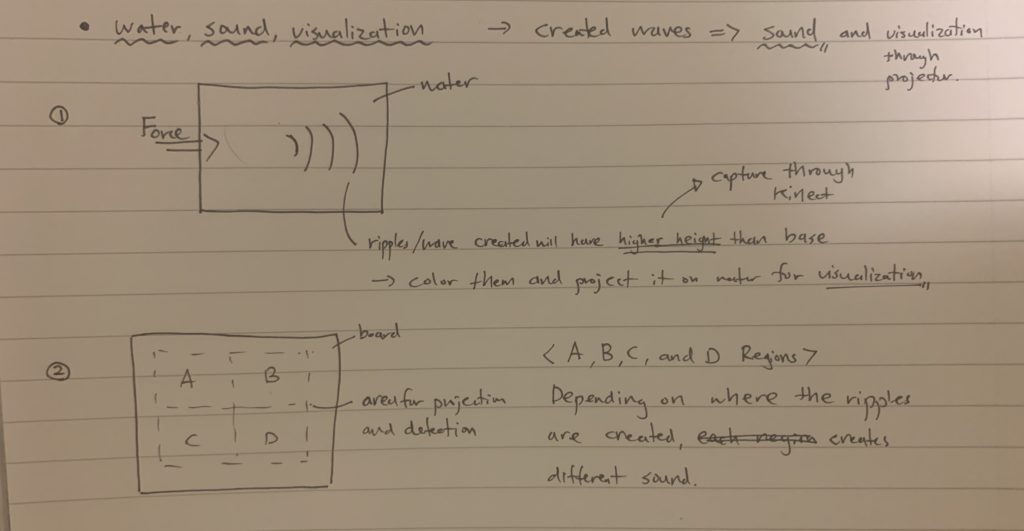
WaterBox is a musical loop station where depending on the user’s physical interaction with water plays different loops either individually or simultaneously. And, the track type changes depending on the roughness of the waves and ripples of the water surface. The final product is created using Kinect v2 to capture the waves of the water surface by its depth, and Touche Advanced Touch Sensor with Arduino for the capacitative sensor and interaction with water. Through the WaterBox, I wanted to share the rich feeling of interacting with water and fun of creating different music with physical motion of your hands in the water.
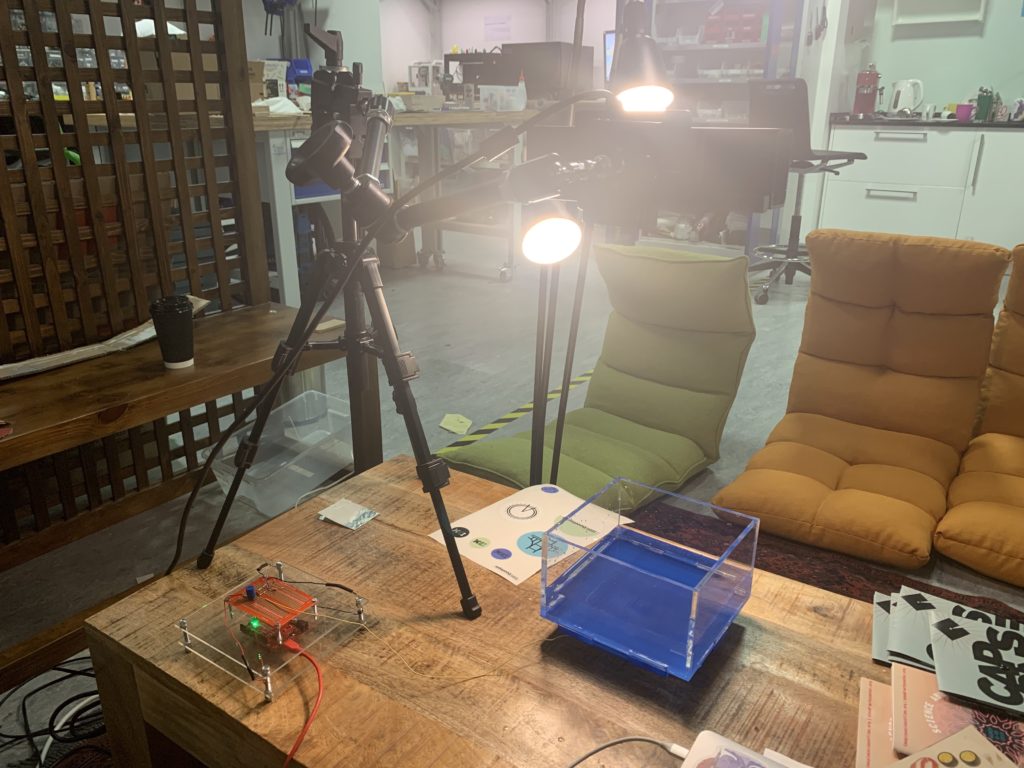
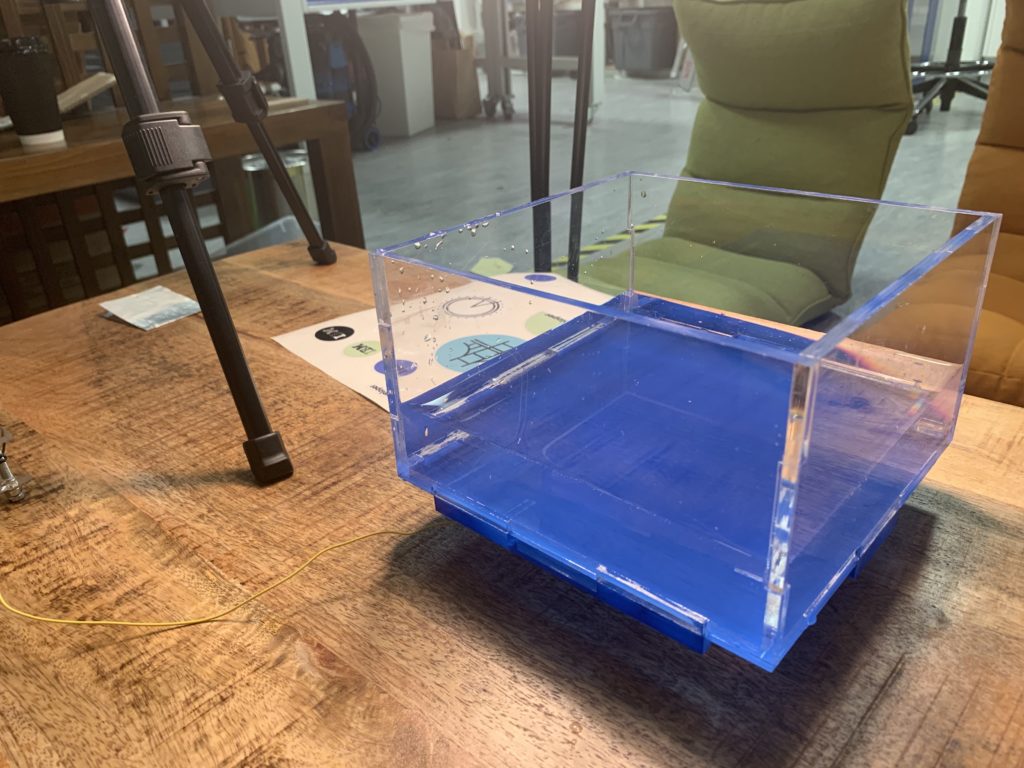
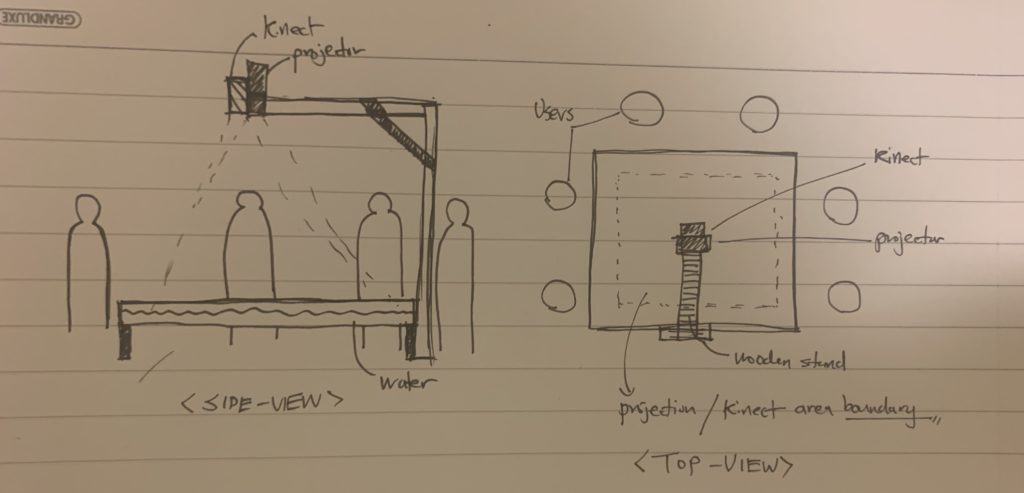
In terms of technical side, the project entails the use of Arduino Uno, a Kinect v2, a container to contain shallow level of water, and a stand that will hold the Kinect in place above the container pointing towards the water. The container was created with transparent acrylic with 18cm x 18cm x 15cm in dimension where the bottom was colored blue for clear detection of the Kinect v2.
The ideal instance of a user interaction would be where users would play around with the water, creating different waves and ripples on the surface. And, depending on the number of fingers (or, to be more precise, the surface area of your hand), different loops will be played on top of one another. Meanwhile, the kinect will capture the depth of the water, and depending on the roughness of the waves, it will change the track of the loops played.
Here are some of user-testing footages:
Development Stages
Initial Stage of using water with Kinect & Sound
Connecting Touche Sensor with Water & Sound
<Source Code>
Processing*
- Main Code
- Graph Class Library (Touche Advance Sensor)
- Serial Link (Touche Advanced Sensor)
import org.openkinect.processing.*;
import processing.sound.*;
int trackType = 6;
int trackCount = 4;
int currentTrackType = 0;
int counter = 0;
String trackName;
/*
============ Touche Advanced Touch Sensor ==============
Source: https://github.com/Illutron/AdvancedTouchSensing
========================================================
*/
Graph MyArduinoGraph = new Graph(150, 80, 500, 300, color (200, 20, 20));
float[][] gesturePoints = new float[4][2];
float[] gestureDist = new float[4];
String[] names = {"Nothing", "One Finger", "Two Finger", "Hand In Water"};
/* ===================================================== */
/* ==== Music Loops ==== */
SoundFile[][] soundPlayers = new SoundFile[trackType][trackCount];
//array to hold the volumes/rate for each track
float[] volumes = new float[trackCount];
//array to hold the volume/rate destinations, to smoothly fade in and out
float[] volumeDestinations = new float[trackCount];
/* ===================== */
/* ==== Kinect Code ==== */
Kinect2 kinect2;
// Min & Max Threshold for Calibration
float minThresh = 570;
float maxThresh = 690;
boolean isSwitched;
PImage img, video;
/* ====================== */
void setup() {
size(1000, 900);
// ==== Touche Setup Code ==== //
PortSelected=8;
SerialPortSetup();
// ============================ //
for (int j=0; j < 6; j++)
{
// ==== NAMING EACH TRACK IN THE SOUND PLAYER 2D ARRAY ==== //
if (j==0)
{
trackName = "deep";
}
else if (j==1)
{
trackName = "edm";
}
else if (j==2)
{
trackName = "hiphop";
}
else if (j==3)
{
trackName = "jazz";
}
else if (j==4)
{
trackName = "latin";
}
else {
trackName = "slow";
}
for (int i=0; i < soundPlayers[j].length; i++)
{
String name = trackName;
name += str(i);
name += ".wav";
println(name);
soundPlayers[j][i] = new SoundFile(this, name);
soundPlayers[j][i].loop();
soundPlayers[j][i].amp(0.001);
volumes[i]=0;
volumeDestinations[i]=0;
}
}
// Kinect Initialization
kinect2 = new Kinect2(this);
kinect2.initRegistered();
kinect2.initDepth();
kinect2.initDevice();
img = createImage(kinect2.depthWidth, kinect2.depthHeight, RGB);
isSwitched = false;
}
void draw() {
background(255);
int pixelCount = 0;
float minDepthLevel = maxThresh;
// Getting soundIndex for Touche Sensor
int soundIndex = advancedTouch();
/* ===================================================== */
img.loadPixels();
video = kinect2.getRegisteredImage();
int[] depth = kinect2.getRawDepth();
// Detect Pixels using Kinect
for (int x = 0; x < kinect2.depthWidth; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < kinect2.depthHeight; y++)
{
int index = x + y * kinect2.depthWidth;
int d = depth[index];
if (d > minThresh
&& d < maxThresh
&& red(video.pixels[index]) < 100
&& green(video.pixels[index]) > 180
&& blue(video.pixels[index]) > 170
// Boundaries to capture only the box on the screen
&& 215 < x
&& 350 > x
&& 125 < y
&& 265 > y
) {
pixelCount++;
img.pixels[index] = color(red(video.pixels[index]), green(video.pixels[index]), blue(video.pixels[index]));
if (d < minDepthLevel)
{
minDepthLevel = d;
}
}
else
{
img.pixels[index] = color(0);
}
}
}
/* ========DEBUG CODE======== */
int mouseIndex = mouseX%kinect2.depthWidth + mouseY%kinect2.depthHeight * kinect2.depthWidth;
text(red(video.pixels[mouseIndex]), 600, 600);
text(green(video.pixels[mouseIndex]), 600, 650);
text(blue(video.pixels[mouseIndex]), 600, 700);
text(mouseX, 600, 750);
text(mouseY-480, 680, 750);
text(pixelCount, 600, 780);
text(minDepthLevel, 680, 780);
text(currentTrackType, 880, 780);
/* ========================== */
img.updatePixels();
// Uncomment below if you want to see whether the Kinect is catching the water pixels
//image(img, 0, 480);
noStroke();
/* ========== Calibration Needed depending on space / light ========== */
// If the catched pixcelCount is in between 300 and 400 & the whole hand is in the water,
// then change the track type.
if (
pixelCount >= 300
&& pixelCount <= 400
&& minDepthLevel <= 590
&&soundIndex == 3
&& !isSwitched)
{
counter++;
if(counter > 800) {
isSwitched = true;
currentTrackType++;
currentTrackType %= 6;
}
}
else if (isSwitched)
{
isSwitched = false;
counter = 0;
}
/* =================================================================== */
if (soundIndex > 1)
{
for (int i=1; i< soundIndex+1; i++)
{
volumeDestinations[i-1] = 1;
if (soundIndex == 3)
{
volumeDestinations[i] = 1;
}
}
}
else if (soundIndex == 1)
{
volumeDestinations[0] = 1;
}
for (int j=0; j<soundPlayers.length; j++)
{
for (int i=0; i<soundPlayers[j].length; i++)
{
if (j != currentTrackType)
{
// set other tracks amplitude to zero
soundPlayers[j][i].amp(0);
}
else
{
//set volume
volumes[i]=smoothing(volumes[i], volumeDestinations[i]);
soundPlayers[j][i].amp(volumes[i]);
//continuously fade volume out
volumeDestinations[i]-=.1;
//constrian the fade out to 0
volumeDestinations[i] = constrain(volumeDestinations[i],0,1);
}
}
}
}
//smoothing for fading in and out
float smoothing(float current, float destination) {
current += (destination-current)*.5;
return current;
}
int advancedTouch() {
/* ===============================================================
Touche Advanced Touch Sensor Code
=============================================================== */
if ( DataRecieved3 ) {
pushMatrix();
pushStyle();
MyArduinoGraph.yMax=600;
MyArduinoGraph.yMin=-200;
MyArduinoGraph.xMax=int (max(Time3));
//MyArduinoGraph.DrawAxis();
MyArduinoGraph.smoothLine(Time3, Voltage3);
popStyle();
popMatrix();
/* ====================================================================
Gesture compare
==================================================================== */
float totalDist = 0;
int currentMax = 0;
float currentMaxValue = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4;i++) {
//println("Index: " + i);
//println(gesturePoints[i][0], gesturePoints[i][1]);
// Calibration for each category
if (mousePressed && mouseX > 750 && mouseX<800 && mouseY > 100*(i+1) && mouseY < 100*(i+1) + 50)
{
fill(255, 0, 0);
gesturePoints[i][0] = Time3[MyArduinoGraph.maxI];
gesturePoints[i][1] = Voltage3[MyArduinoGraph.maxI];
}
else
{
fill(255, 255, 255);
}
//calucalte individual dist
gestureDist[i] = dist(Time3[MyArduinoGraph.maxI], Voltage3[MyArduinoGraph.maxI], gesturePoints[i][0], gesturePoints[i][1]);
totalDist = totalDist + gestureDist[i];
if(gestureDist[i] < currentMaxValue || i == 0)
{
currentMax = i;
currentMaxValue = gestureDist[i];
}
}
totalDist=totalDist/3;
for (int i = 0; i < 4;i++)
{
float currentAmount = 0;
currentAmount = 1-gestureDist[i]/totalDist;
if(currentMax == i) {
fill(0,0,0);
//text(names[i],50,450);
fill(currentAmount*255.0f, 0, 0);
}
else {
fill(255,255,255);
}
stroke(0, 0, 0);
rect(750, 100 * (i+1), 50, 50);
fill(0,0,0);
textSize(30);
text(names[i],810,100 * (i+1)+25);
fill(255, 0, 0);
rect(800,100* (i+1), max(0,currentAmount*50),50);
}
return currentMax;
}
return 0;
}
/* =================================================================================
The Graph class contains functions and variables that have been created to draw
graphs. Here is a quick list of functions within the graph class:
Graph(int x, int y, int w, int h,color k)
DrawAxis()
Bar([])
smoothLine([][])
DotGraph([][])
LineGraph([][])
=================================================================================*/
class Graph
{
float maxY = 0;
float maxX = 0;
int maxI = 0;
boolean Dot=true; // Draw dots at each data point if true
boolean RightAxis; // Draw the next graph using the right axis if true
boolean ErrorFlag=false; // If the time array isn't in ascending order, make true
boolean ShowMouseLines=true; // Draw lines and give values of the mouse position
int xDiv=5, yDiv=5; // Number of sub divisions
int xPos, yPos; // location of the top left corner of the graph
int Width, Height; // Width and height of the graph
color GraphColor;
color BackgroundColor=color(255);
color StrokeColor=color(180);
String Title="Title"; // Default titles
String xLabel="x - Label";
String yLabel="y - Label";
float yMax=1024, yMin=0; // Default axis dimensions
float xMax=10, xMin=0;
float yMaxRight=1024, yMinRight=0;
Graph(int x, int y, int w, int h, color k) { // The main declaration function
xPos = x;
yPos = y;
Width = w;
Height = h;
GraphColor = k;
}
void DrawAxis() {
/* =========================================================================================
Main axes Lines, Graph Labels, Graph Background
========================================================================================== */
fill(BackgroundColor);
color(0);
stroke(StrokeColor);
strokeWeight(1);
int t=60;
rect(xPos-t*1.6, yPos-t, Width+t*2.5, Height+t*2); // outline
textAlign(CENTER);
textSize(18);
float c=textWidth(Title);
fill(BackgroundColor);
color(0);
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(1);
rect(xPos+Width/2-c/2, yPos-35, c, 0); // Heading Rectangle
fill(0);
text(Title, xPos+Width/2, yPos-37); // Heading Title
textAlign(CENTER);
textSize(14);
text(xLabel, xPos+Width/2, yPos+Height+t/1.5); // x-axis Label
rotate(-PI/2); // rotate -90 degrees
text(yLabel, -yPos-Height/2, xPos-t*1.6+20); // y-axis Label
rotate(PI/2); // rotate back
textSize(10);
noFill();
stroke(0);
smooth();
strokeWeight(1);
//Edges
line(xPos-3, yPos+Height, xPos-3, yPos); // y-axis line
line(xPos-3, yPos+Height, xPos+Width+5, yPos+Height); // x-axis line
stroke(200);
if (yMin<0) {
line(xPos-7, // zero line
yPos+Height-(abs(yMin)/(yMax-yMin))*Height, //
xPos+Width,
yPos+Height-(abs(yMin)/(yMax-yMin))*Height
);
}
if (RightAxis) { // Right-axis line
stroke(0);
line(xPos+Width+3, yPos+Height, xPos+Width+3, yPos);
}
/* =========================================================================================
Sub-devisions for both axes, left and right
========================================================================================== */
stroke(0);
for (int x=0; x<=xDiv; x++) {
/* =========================================================================================
x-axis
========================================================================================== */
line(float(x)/xDiv*Width+xPos-3, yPos+Height, // x-axis Sub devisions
float(x)/xDiv*Width+xPos-3, yPos+Height+5);
textSize(10); // x-axis Labels
String xAxis=str(xMin+float(x)/xDiv*(xMax-xMin)); // the only way to get a specific number of decimals
String[] xAxisMS=split(xAxis, '.'); // is to split the float into strings
text(xAxisMS[0]+"."+xAxisMS[1].charAt(0), // ...
float(x)/xDiv*Width+xPos-3, yPos+Height+15); // x-axis Labels
}
/* =========================================================================================
left y-axis
========================================================================================== */
for (int y=0; y<=yDiv; y++) {
line(xPos-3, float(y)/yDiv*Height+yPos, // ...
xPos-7, float(y)/yDiv*Height+yPos); // y-axis lines
textAlign(RIGHT);
fill(20);
String yAxis=str(yMin+float(y)/yDiv*(yMax-yMin)); // Make y Label a string
String[] yAxisMS=split(yAxis, '.'); // Split string
text(yAxisMS[0]+"."+yAxisMS[1].charAt(0), // ...
xPos-15, float(yDiv-y)/yDiv*Height+yPos+3); // y-axis Labels
/* =========================================================================================
right y-axis
========================================================================================== */
if (RightAxis) {
color(GraphColor);
stroke(GraphColor);
fill(20);
line(xPos+Width+3, float(y)/yDiv*Height+yPos, // ...
xPos+Width+7, float(y)/yDiv*Height+yPos); // Right Y axis sub devisions
textAlign(LEFT);
String yAxisRight=str(yMinRight+float(y)/ // ...
yDiv*(yMaxRight-yMinRight)); // convert axis values into string
String[] yAxisRightMS=split(yAxisRight, '.'); //
text(yAxisRightMS[0]+"."+yAxisRightMS[1].charAt(0), // Right Y axis text
xPos+Width+15, float(yDiv-y)/yDiv*Height+yPos+3); // it's x,y location
noFill();
}
stroke(0);
}
}
/* =========================================================================================
Bar graph
========================================================================================== */
void Bar(float[] a, int from, int to) {
stroke(GraphColor);
fill(GraphColor);
if (from<0) { // If the From or To value is out of bounds
for (int x=0; x<a.length; x++) { // of the array, adjust them
rect(int(xPos+x*float(Width)/(a.length)),
yPos+Height-2,
Width/a.length-2,
-a[x]/(yMax-yMin)*Height);
}
}
else {
for (int x=from; x<to; x++) {
rect(int(xPos+(x-from)*float(Width)/(to-from)),
yPos+Height-2,
Width/(to-from)-2,
-a[x]/(yMax-yMin)*Height);
}
}
}
void Bar(float[] a ) {
stroke(GraphColor);
fill(GraphColor);
for (int x=0; x<a.length; x++) { // of the array, adjust them
rect(int(xPos+x*float(Width)/(a.length)),
yPos+Height-2,
Width/a.length-2,
-a[x]/(yMax-yMin)*Height);
}
}
/* =========================================================================================
Dot graph
========================================================================================== */
void DotGraph(float[] x, float[] y) {
for (int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(GraphColor);
noFill();
smooth();
ellipse(
xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height,
2, 2
);
}
}
/* =========================================================================================
Streight line graph
========================================================================================== */
void LineGraph(float[] x, float[] y) {
for (int i=0; i<(x.length-1); i++) {
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(GraphColor);
noFill();
smooth();
line(xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height,
xPos+(x[i+1]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i+1]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height);
}
}
/* =========================================================================================
smoothLine
========================================================================================== */
void smoothLine(float[] x, float[] y) {
float tempyMax=yMax, tempyMin=yMin;
if (RightAxis) {
yMax=yMaxRight;
yMin=yMinRight;
}
int xlocation=0, ylocation=0;
// if(!ErrorFlag |true ){ // sort out later!
beginShape();
strokeWeight(6);
stroke(GraphColor);
noFill();
smooth();
maxY = 0;
//find max
for (int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
if (maxY < y[i])
{
maxY =y[i];
maxI = i;
}
}
for (int i=0; i<x.length; i++) {
/* ===========================================================================
Check for errors-> Make sure time array doesn't decrease (go back in time)
===========================================================================*/
if (i<x.length-1) {
if (x[i]>x[i+1]) {
ErrorFlag=true;
}
}
/* =================================================================================
First and last bits can't be part of the curve, no points before first bit,
none after last bit. So a streight line is drawn instead
================================================================================= */
if (i==0 || i==x.length-2)line(xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height,
xPos+(x[i+1]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i+1]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height);
/* =================================================================================
For the rest of the array a curve (spline curve) can be created making the graph
smooth.
================================================================================= */
curveVertex( xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height);
/* =================================================================================
If the Dot option is true, Place a dot at each data point.
================================================================================= */
if (i == maxI)
{
ellipse(
xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height,
20, 20
);
}
if (Dot)ellipse(
xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width,
yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height,
2, 2
);
/* =================================================================================
Highlights points closest to Mouse X position
=================================================================================*/
if ( abs(mouseX-(xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width))<5 ) {
float yLinePosition = yPos+Height-(y[i]/(yMax-yMin)*Height)+(yMin)/(yMax-yMin)*Height;
float xLinePosition = xPos+(x[i]-x[0])/(x[x.length-1]-x[0])*Width;
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(240);
// line(xPos,yLinePosition,xPos+Width,yLinePosition);
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(GraphColor);
ellipse(xLinePosition, yLinePosition, 4, 4);
}
}
endShape();
yMax=tempyMax;
yMin=tempyMin;
float xAxisTitleWidth=textWidth(str(map(xlocation, xPos, xPos+Width, x[0], x[x.length-1])));
if ((mouseX>xPos&mouseX<(xPos+Width))&(mouseY>yPos&mouseY<(yPos+Height))) {
if (ShowMouseLines) {
// if(mouseX<xPos)xlocation=xPos;
if (mouseX>xPos+Width)xlocation=xPos+Width;
else xlocation=mouseX;
stroke(200);
strokeWeight(0.5);
fill(255);
color(50);
// Rectangle and x position
line(xlocation, yPos, xlocation, yPos+Height);
rect(xlocation-xAxisTitleWidth/2-10, yPos+Height-16, xAxisTitleWidth+20, 12);
textAlign(CENTER);
fill(160);
text(map(xlocation, xPos, xPos+Width, x[0], x[x.length-1]), xlocation, yPos+Height-6);
// if(mouseY<yPos)ylocation=yPos;
if (mouseY>yPos+Height)ylocation=yPos+Height;
else ylocation=mouseY;
// Rectangle and y position
stroke(200);
strokeWeight(0.5);
fill(255);
color(50);
line(xPos, ylocation, xPos+Width, ylocation);
//int yAxisTitleWidth=int(textWidth(str(map(ylocation, yPos, yPos+Height, y[0], y[y.length-1]))) );
rect(xPos-15+3, ylocation-6, -60, 12);
textAlign(RIGHT);
fill(GraphColor);//StrokeColor
// text(map(ylocation,yPos+Height,yPos,yMin,yMax),xPos+Width+3,yPos+Height+4);
text(map(ylocation, yPos+Height, yPos, yMin, yMax), xPos -15, ylocation+4);
if (RightAxis) {
stroke(200);
strokeWeight(0.5);
fill(255);
color(50);
rect(xPos+Width+15-3, ylocation-6, 60, 12);
textAlign(LEFT);
fill(160);
text(map(ylocation, yPos+Height, yPos, yMinRight, yMaxRight), xPos+Width+15, ylocation+4);
}
noStroke();
noFill();
}
}
}
void smoothLine(float[] x, float[] y, float[] z, float[] a ) {
GraphColor=color(188, 53, 53);
smoothLine(x, y);
GraphColor=color(193-100, 216-100, 16);
smoothLine(z, a);
}
}
import processing.serial.*;
int SerialPortNumber=2;
int PortSelected=2;
/* =================================================================================
Global variables
=================================================================================*/
int xValue, yValue, Command;
boolean Error=true;
boolean UpdateGraph=true;
int lineGraph;
int ErrorCounter=0;
int TotalRecieved=0;
/* =================================================================================
Local variables
=================================================================================*/
boolean DataRecieved1=false, DataRecieved2=false, DataRecieved3=false;
float[] DynamicArrayTime1, DynamicArrayTime2, DynamicArrayTime3;
float[] Time1, Time2, Time3;
float[] Voltage1, Voltage2, Voltage3;
float[] current;
float[] DynamicArray1, DynamicArray2, DynamicArray3;
float[] PowerArray= new float[0]; // Dynamic arrays that will use the append()
float[] DynamicArrayPower = new float[0]; // function to add values
float[] DynamicArrayTime= new float[0];
String portName;
String[] ArrayOfPorts=new String[SerialPortNumber];
boolean DataRecieved=false, Data1Recieved=false, Data2Recieved=false;
int incrament=0;
int NumOfSerialBytes=8; // The size of the buffer array
int[] serialInArray = new int[NumOfSerialBytes]; // Buffer array
int serialCount = 0; // A count of how many bytes received
int xMSB, xLSB, yMSB, yLSB; // Bytes of data
Serial myPort; // The serial port object
/* =================================================================================
A once off serail port setup function. In this case the selection of the speed,
the serial port and clearing the serial port buffer
=================================================================================*/
void SerialPortSetup() {
// text(Serial.list().length,200,200);
portName= Serial.list()[PortSelected];
ArrayOfPorts=Serial.list();
println(ArrayOfPorts);
myPort = new Serial(this, portName, 115200);
//delay(50);
//myPort.clear();
//myPort.buffer(20);
}
/* ============================================================
serialEvent will be called when something is sent to the
serial port being used.
============================================================ */
void serialEvent(Serial myPort) {
while (myPort.available ()>0)
{
/* ============================================================
Read the next byte that's waiting in the buffer.
============================================================ */
int inByte = myPort.read();
myPort.write(0);
if (inByte==0)serialCount=0;
if (inByte>255) {
println(" inByte = "+inByte);
exit();
}
// Add the latest byte from the serial port to array:
serialInArray[serialCount] = inByte;
serialCount++;
Error=true;
if (serialCount >= NumOfSerialBytes ) {
serialCount = 0;
TotalRecieved++;
int Checksum=0;
// Checksum = (Command + yMSB + yLSB + xMSB + xLSB + zeroByte)%255;
for (int x=0; x<serialInArray.length-1; x++) {
Checksum=Checksum+serialInArray[x];
}
Checksum=Checksum%255;
if (Checksum==serialInArray[serialInArray.length-1]) {
Error = false;
DataRecieved=true;
}
else {
Error = true;
// println("Error: "+ ErrorCounter +" / "+ TotalRecieved+" : "+float(ErrorCounter/TotalRecieved)*100+"%");
DataRecieved=false;
ErrorCounter++;
println("Error: "+ ErrorCounter +" / "+ TotalRecieved+" : "+float(ErrorCounter/TotalRecieved)*100+"%");
}
}
if (!Error) {
int zeroByte = serialInArray[6];
// println (zeroByte & 2);
xLSB = serialInArray[3];
if ( (zeroByte & 1) == 1) xLSB=0;
xMSB = serialInArray[2];
if ( (zeroByte & 2) == 2) xMSB=0;
yLSB = serialInArray[5];
if ( (zeroByte & 4) == 4) yLSB=0;
yMSB = serialInArray[4];
if ( (zeroByte & 8) == 8) yMSB=0;
// println( "0\tCommand\tyMSB\tyLSB\txMSB\txLSB\tzeroByte\tsChecksum");
// println(serialInArray[0]+"\t"+Command +"\t"+ yMSB +"\t"+ yLSB +"\t"+ xMSB +"\t"+ xLSB+"\t" +zeroByte+"\t"+ serialInArray[7]);
// >=====< combine bytes to form large integers >==================< //
Command = serialInArray[1];
xValue = xMSB << 8 | xLSB; // Get xValue from yMSB & yLSB
yValue = yMSB << 8 | yLSB; // Get yValue from xMSB & xLSB
// println(Command+ " "+xValue+" "+ yValue+" " );
/*
How that works: if xMSB = 10001001 and xLSB = 0100 0011
xMSB << 8 = 10001001 00000000 (shift xMSB left by 8 bits)
xLSB = 01000011
xLSB | xMSB = 10001001 01000011 combine the 2 bytes using the logic or |
xValue = 10001001 01000011 now xValue is a 2 byte number 0 -> 65536
*/
/* ==================================================================
Command, xValue & yValue have now been recieved from the chip
================================================================== */
switch(Command) {
/* ==================================================================
Recieve array1 and array2 from chip, update oscilloscope
================================================================== */
case 1: // Data is added to dynamic arrays
DynamicArrayTime3=append( DynamicArrayTime3, (xValue) );
DynamicArray3=append( DynamicArray3, (yValue) );
break;
case 2: // An array of unknown size is about to be recieved, empty storage arrays
DynamicArrayTime3= new float[0];
DynamicArray3= new float[0];
break;
case 3: // Array has finnished being recieved, update arrays being drawn
Time3=DynamicArrayTime3;
Voltage3=DynamicArray3;
// println(Voltage3.length);
DataRecieved3=true;
break;
/* ==================================================================
Recieve array2 and array3 from chip
================================================================== */
case 4: // Data is added to dynamic arrays
DynamicArrayTime2=append( DynamicArrayTime2, xValue );
DynamicArray2=append( DynamicArray2, (yValue-16000.0)/32000.0*20.0 );
break;
case 5: // An array of unknown size is about to be recieved, empty storage arrays
DynamicArrayTime2= new float[0];
DynamicArray2= new float[0];
break;
case 6: // Array has finnished being recieved, update arrays being drawn
Time2=DynamicArrayTime2;
current=DynamicArray2;
DataRecieved2=true;
break;
/* ==================================================================
Recieve a value of calculated power consumption & add it to the
PowerArray.
================================================================== */
case 20:
PowerArray=append( PowerArray, yValue );
break;
case 21:
DynamicArrayTime=append( DynamicArrayTime, xValue );
DynamicArrayPower=append( DynamicArrayPower, yValue );
break;
}
}
}
redraw();
// }
}
Arduino* (Touche Advanced Sensor)
//****************************************************************************************
// Illutron take on Disney style capacitive touch sensor using only passives and Arduino
// Dzl 2012
//****************************************************************************************
// 10n
// PIN 9 --[10k]-+-----10mH---+--||-- OBJECT
// | |
// 3.3k |
// | V 1N4148 diode
// GND |
// |
//Analog 0 ---+------+--------+
// | |
// 100pf 1MOmhm
// | |
// GND GND
#define SET(x,y) (x |=(1<<y)) //-Bit set/clear macros
#define CLR(x,y) (x &= (~(1<<y))) // |
#define CHK(x,y) (x & (1<<y)) // |
#define TOG(x,y) (x^=(1<<y)) //-+
#define N 160 //How many frequencies
float results[N]; //-Filtered result buffer
float freq[N]; //-Filtered result buffer
int sizeOfArray = N;
void setup() {
TCCR1A=0b10000010; //-Set up frequency generator
TCCR1B=0b00011001; //-+
ICR1=110;
OCR1A=55;
pinMode(9,OUTPUT); //-Signal generator pin
pinMode(8,OUTPUT); //-Sync (test) pin
Serial.begin(115200);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) //-Preset results
results[i]=0; //-+
}
void loop()
{
unsigned int d;
int counter = 0;
for(unsigned int d=0;d<N;d++) {
int v=analogRead(0); //-Read response signal
CLR(TCCR1B,0); //-Stop generator
TCNT1=0; //-Reload new frequency
ICR1=d; // |
OCR1A=d/2; //-+
SET(TCCR1B,0); //-Restart generator
results[d]=results[d]*0.5+(float)(v)*0.5; //Filter results
freq[d] = d;
}
PlottArray(1,freq,results);
TOG(PORTB,0); //-Toggle pin 8 after each sweep (good for scope)
}
byte yMSB=0, yLSB=0, xMSB=0, xLSB=0, zeroByte=128, Checksum=0;
void SendData(int Command, unsigned int yValue,unsigned int xValue){
/* >=================================================================<
y = 01010100 11010100 (x & y are 2 Byte integers)
yMSB yLSB send seperately -> reciever joins them
>=================================================================< */
yLSB=lowByte(yValue);
yMSB=highByte(yValue);
xLSB=lowByte(xValue);
xMSB=highByte(xValue);
/* >=================================================================<
Only the very first Byte may be a zero, this way allows the computer
to know that if a Byte recieved is a zero it must be the start byte.
If data bytes actually have a value of zero, They are given the value
one and the bit in the zeroByte that represents that Byte is made
high.
>=================================================================< */
zeroByte = 128; // 10000000
if(yLSB==0){ yLSB=1; zeroByte=zeroByte+1;} // Make bit 1 high
if(yMSB==0){ yMSB=1; zeroByte=zeroByte+2;} // make bit 2 high
if(xLSB==0){ xLSB=1; zeroByte=zeroByte+4;} // make bit 3 high
if(xMSB==0){ xMSB=1; zeroByte=zeroByte+8;} // make bit 4 high
/* >=================================================================<
Calculate the remainder of: sum of all the Bytes divided by 255
>=================================================================< */
Checksum = (Command + yMSB + yLSB + xMSB + xLSB + zeroByte)%255;
if( Checksum !=0 ){
int inByte = Serial.read();
Serial.write(byte(0)); // send start bit
Serial.write(byte(Command)); // command eg: Which Graph is this data for
Serial.write(byte(yMSB)); // Y value's most significant byte
Serial.write(byte(yLSB)); // Y value's least significant byte
Serial.write(byte(xMSB)); // X value's most significant byte
Serial.write(byte(xLSB)); // X value's least significant byte
Serial.write(byte(zeroByte)); // Which values have a zero value
Serial.write(byte(Checksum)); // Error Checking Byte
}
}
void PlottArray(unsigned int Cmd,float Array1[],float Array2[]){
SendData(Cmd+1, 1,1); // Tell PC an array is about to be sent
delay(1);
for(int x=0; x < sizeOfArray; x++){ // Send the arrays
SendData(Cmd, round(Array1[x]),round(Array2[x]));
//delay(1);
}
SendData(Cmd+2, 1,1); // Confirm arrrays have been sent
}