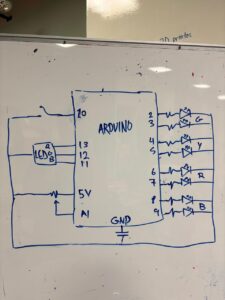
I designed a simple interactive game using LEDs, a potentiometer, and a digital switch. The setup has two rows of LED pairs, each pair matching in color. The potentiometer controls the start point. When I rotate it, the highlighted position shifts across the pairs and cycles through them.
When I press the digital switch, one of the two lit LEDs starts moving quickly along its row. Pressing the button again stops it. If the moving LED stops exactly on the matching position of the other fixed LED, a green verdict LED turns on to show success. If not, a red verdict LED lights up, and the game resets to the start point.
It’s a fun, simple matching game that combines timing, control, and basic electronics.
Code:
// — Pin Definitions —
// LED Rows (G, Y, R, B)
const int fixedRowPins[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
const int cyclingRowPins[] = {3, 5, 7, 9};
// RGB Feedback LED Pins
const int RGB_RED_PIN = 11;
const int RGB_GREEN_PIN = 12;
const int RGB_BLUE_PIN = 13;
// Input Pins
const int POT_PIN = A1;
const int BUTTON_PIN = 10;
// — Game Logic Variables —
// Game State: false = waiting/potentiometer mode, true = cycling/active mode
bool gameIsActive = false;
// Stores the color index (0-3) when the game starts
int targetColorIndex = 0;
// Stores the current color index (0-3) of the cycling light
int currentCyclingIndex = 0;
// — Timing Variables for Non-Blocking Cycling —
unsigned long previousCycleMillis = 0;
const int CYCLE_SPEED_MS = 80; // How fast the light cycles (lower is faster)
const int VERDICT_DISPLAY_MS = 2000; // How long to show Red/Green verdict
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging
// Set all 8 game LED pins to OUTPUT
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pinMode(fixedRowPins[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode(cyclingRowPins[i], OUTPUT);
}
// Set RGB LED pins to OUTPUT
pinMode(RGB_RED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RGB_GREEN_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RGB_BLUE_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Set button pin with an internal pull-up resistor
// The pin will be HIGH when not pressed and LOW when pressed
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
// Read the button state
bool buttonPressed = (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW);
// — Main Game Logic: Two States —
// STATE 1: Game is NOT active. Control LEDs with the potentiometer.
if (!gameIsActive) {
handlePotentiometer(); // Light up LED pair based on pot
// Check if the button is pressed to START the game
if (buttonPressed) {
Serial.println(“Button pressed! Starting game…”);
// Lock in the current color from the potentiometer
targetColorIndex = getPotIndex();
gameIsActive = true; // Switch to the active game state
turnRgbOff(); // Ensure verdict light is off
// Wait for the button to be released to avoid misfires
while(digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW);
delay(50); // Simple debounce
}
}
// STATE 2: Game IS active. Cycle the lights and wait for the player’s timing.
else {
cycleLights(); // Handle the light cycling logic
// Check if the button is pressed to STOP the cycle and check the verdict
if (buttonPressed) {
Serial.println(“Timing button pressed!”);
// The currentCyclingIndex is the player’s selection
checkVerdict();
gameIsActive = false; // Game is over, switch back to potentiometer mode
// Wait for button release
while(digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW);
delay(50); // Simple debounce
}
}
}
// — Helper Functions —
// Reads potentiometer and lights up the corresponding LED pair
void handlePotentiometer() {
int potIndex = getPotIndex();
lightLedPair(potIndex);
}
// Reads the potentiometer and maps its value to an index from 0 to 3
int getPotIndex() {
int potValue = analogRead(POT_PIN); // Reads value from 0-1023
// Map the 0-1023 range to four sub-ranges (0, 1, 2, 3)
int index = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 3);
return index;
}
// Lights one pair of LEDs based on an index (0-3)
void lightLedPair(int index) {
turnAllGameLedsOff();
digitalWrite(fixedRowPins[index], HIGH);
digitalWrite(cyclingRowPins[index], HIGH);
}
// Manages the fast, non-blocking cycling of the second row of LEDs
void cycleLights() {
// This uses millis() to avoid delay() so we can still read the button
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis – previousCycleMillis >= CYCLE_SPEED_MS) {
previousCycleMillis = currentMillis; // Reset the timer
// Move to the next LED in the cycle
currentCyclingIndex++;
if (currentCyclingIndex > 3) {
currentCyclingIndex = 0; // Loop back to the start
}
// Update the lights
turnAllGameLedsOff();
digitalWrite(fixedRowPins[targetColorIndex], HIGH); // Keep fixed LED on
digitalWrite(cyclingRowPins[currentCyclingIndex], HIGH); // Light the current cycling LED
}
}
// Checks if the player’s timing was correct and shows the verdict
void checkVerdict() {
if (currentCyclingIndex == targetColorIndex) {
Serial.println(“Verdict: CORRECT!”);
showVerdict(true); // Show green light
} else {
Serial.println(“Verdict: WRONG!”);
showVerdict(false); // Show red light
}
}
// Lights up the RGB LED Green for correct, Red for incorrect
void showVerdict(bool isCorrect) {
turnAllGameLedsOff(); // Turn off game lights to focus on verdict
if (isCorrect) {
// Light RGB GREEN
digitalWrite(RGB_RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(RGB_GREEN_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RGB_BLUE_PIN, LOW);
} else {
// Light RGB RED
digitalWrite(RGB_RED_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RGB_GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(RGB_BLUE_PIN, LOW);
}
delay(VERDICT_DISPLAY_MS); // Hold the verdict light
turnRgbOff(); // Turn off the verdict light before returning to the game
}
// — Utility Functions —
// Turns off all 8 game LEDs
void turnAllGameLedsOff() {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
digitalWrite(fixedRowPins[i], LOW);
digitalWrite(cyclingRowPins[i], LOW);
}
}
// Turns off the RGB LED
void turnRgbOff() {
digitalWrite(RGB_RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(RGB_GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(RGB_BLUE_PIN, LOW);
}