For this week’s assignment, we were asked to complete the three examples we had been tasked with during class. This week’s work was a learning curve on its own. It took a while to get the hang of connecting P5.js and Arduino together after using them both as seperate entities, but seeing them connected was really exciting.
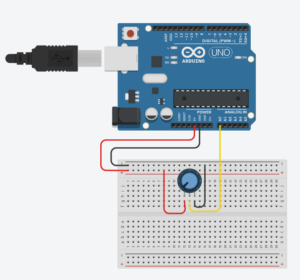
Task 1 – make something that uses only one sensor on Arduino and makes the ellipse in p5 move on the horizontal axis
For this task, I used a potentiometer to get analogue values, then mapped them onto my P5 canvas to make the ellipse move
P5 code:
let serial; // variable for the serial object
let latestData = "waiting for data"; // variable to hold the data
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 400);
// serial constructor
serial = new p5.SerialPort();
// serial port
serial.open('COM6');
// what to do when we get serial data
serial.on('data', gotData);
}
// when data is received in the serial buffer
function gotData() {
let currentString = serial.readLine(); // store the data in a variable
trim(currentString); // get rid of whitespace
if (!currentString) return; // if there's nothing in there, ignore it
console.log(currentString); // print it out
latestData = currentString; // save it to the global variable
}
function draw() {
background(255, 255, 255);
fill(0, 0, 0);
text(latestData, 10, 10); // print the data to the sketch
// using the recieved data to change the x value of the circle
let moveHorizontal = map(latestData, 0, 1023, 0 , width);
ellipse(moveHorizontal, height/2, 100, 100);
}
Arduino code:
const int ledPin = 3; // the pin that the LED is attached to
void setup() {
// initialize the serial communication:
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize the ledPin as an output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
int brightness;
// check if data has been sent from the computer:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the most recent byte (which will be from 0 to 255):
brightness = Serial.read();
// set the brightness of the LED:
analogWrite(ledPin, brightness);
}
}
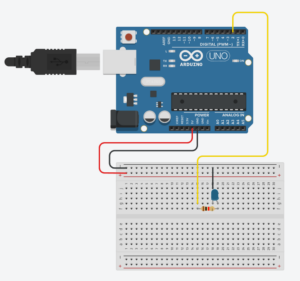
Task 2 – make something that controls the LED brightness from P5
For this task, I created a gradient background on P5, then used the mouseDragged() function to map it onto the LED connected on the Arduino
P5 code:
let serial; // variable for the serial object
let bright = 0; // variable to hold the data we're sending
let dark, light; // variables to hold the bgcolor
function setup() {
createCanvas(512, 512);
// colors for a blue gradient
dim = color(0, 191, 255 ); // light blue
bright = color(0, 0, 128); // dark blue
// serial constructor
serial = new p5.SerialPort();
// serial port
serial.open('COM6');
}
function draw() {
// Create a vertical blue gradient
for (let y = 0; y < height; y++) {
// Directly map the y position to the blue color
let c = map(y, 0, height, dim.levels[2], bright.levels[2]); // Map blue values from dark to light
stroke(c, c, 255); // Set color to blue, vary based on y position
line(0, y, width, y);
}
stroke(255);
strokeWeight(3);
noFill();
ellipse(mouseX, mouseY, 10, 10);
}
function mouseDragged() { // mapping the brightness level based on the position of the mouse
brightLevel = floor(map(mouseY, 0, 512, 0, 255));
// ensuring the brightness level does not exceed the level possible for the LED
brightLevel = constrain(brightLevel, 0, 255);
serial.write(brightLevel);
console.log(brightLevel);
}
Arduino code:
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin where the LED is connected
const int windSensorPin = A0; // Pin for the analog wind sensor
int sensorValue = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as an output
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Check if there is incoming serial data
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char incomingByte = Serial.read(); // Read incoming byte
if (incomingByte == 'O') {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn LED ON
} else if (incomingByte == 'F') {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn LED OFF
}
}
// Read the wind sensor value (adjust if needed)
sensorValue = analogRead(windSensorPin);
// Optionally, print the sensor value for debugging
Serial.println(sensorValue);
delay(100);
}
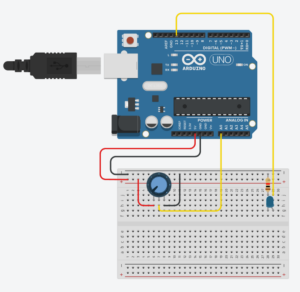
Task 3 – take the gravity wind example (https://editor.p5js.org/aaronsherwood/sketches/I7iQrNCul) and make it so every time the ball bounces one led lights up and then turns off, and you can control the wind from one analog sensor
For this task, I used a potentiometer on the Arduino to send analogue values for the wind in the P5 example. I struggled with having the LED light up in time with the ball bounces, but I ended up using an IF statement within the draw() function which would then send a HIGH or LOW voltage value back to the Arduino
P5 code:
let velocity;
let gravity;
let position;
let acceleration;
let wind;
let drag = 0.99;
let mass = 50;
// new variables added
let windSensorValue = 0;
let serial;
let latestData = "0";
let ledState = false; // true = on, false = off
function setup() {
createCanvas(640, 360);
noFill();
position = createVector(width / 2, 0);
velocity = createVector(0, 0);
acceleration = createVector(0, 0);
gravity = createVector(0, 0.5 * mass);
wind = createVector(0, 0);
// setting up the serial port
serial = new p5.SerialPort();
serial.open('COM6');
serial.on('data', serialEvent);
}
// Arduino data is stored inside the variable latestData
function serialEvent() {
let incoming = serial.readLine();
if (incoming.length > 0) {
latestData = incoming;
}
}
function draw() {
background(255);
// reading the Potentiometer value
// mapping the potentiometer value to wind (either left or right)
let sensorValue = int(latestData);
wind.x = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, -5, 5);
applyForce(wind);
applyForce(gravity);
velocity.add(acceleration);
velocity.mult(drag);
position.add(velocity);
acceleration.mult(0);
ellipse(position.x, position.y, mass, mass);
// Ball hitting ground
if (position.y >= height - mass / 2) {
position.y = height - mass / 2;
velocity.y *= -0.9;
// If touching ground and LED not already on
if (!ledState) {
serial.write('H'); // Turn LED on
ledState = true;
}
} else {
// If in air and LED is on, turn it off
if (ledState) {
serial.write('L'); // Turn LED off
ledState = false;
}
}
}
function applyForce(force) {
let f = p5.Vector.div(force, mass);
acceleration.add(f);
}
function keyPressed() {
if (keyCode == LEFT_ARROW) {
wind.x = -1;
}
if (keyCode == RIGHT_ARROW) {
wind.x = 1;
}
if (key == ' ') {
mass = random(15, 80);
position.y = -mass;
velocity.mult(0);
}
}
Arduino code:
const int ledPin = 13; // LED on pin 13
const int sensorPin = A0; // analog sensor connected to A0
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Read analog sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
Serial.println(sensorValue);
delay(50); // small delay
// Check for incoming commands
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char command = Serial.read();
if (command == 'H') {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else if (command == 'L') {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}
}