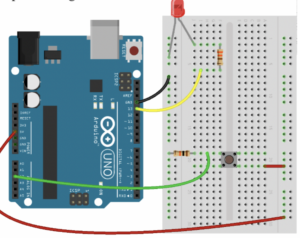
My Arduino code simulates a mini DJ player by incorporating a potentiometer and a switch. The potentiometer, connected to analog input pin A1, emulates a DJ slider or knob, allowing you to control the brightness of an LED connected to PWM pin 11. This provides a visual representation of adjustments such as volume or fading effects.
Meanwhile, the switch, connected to digital input pin A2, mimics a button on the DJ player. When the button is pressed, a yellow light connected to pin 13 is activated briefly, creating a visual cue for a button press or an effect. The code establishes a loop that continuously reads the analog sensor value, and button state, and adjusts LED brightness accordingly, producing a dynamic and interactive simulation of a basic DJ player interface.
It does not look like DJ player in the bright light, and it was hard for me to take a video with one hand and simultaneously press the button with another hand.
int led = 11; //the PMW pin the LED is attached to
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
//declare pin 11 to be output:
pinMode(led,OUTPUT);
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); //yellow light
pinMode(A2, INPUT); //button
}
// put your setup code here, to run once:
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
int sensorValue = analogRead(A1);
//Serial.println(sensorValue);
int buttonState = digitalRead(A2); //button
Serial.println(buttonState);
if (buttonState == 1) {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH);
delay(100);
} else {
digitalWrite(13, LOW);
//delay(300);
}
//set the brightness of pin 11 according to the sensor value/4)
analogWrite(led, sensorValue/4);
//wait for 30 milliseconds to see the diming effect
delay(30);
}
One particularly interesting aspect of the code is the use of the analog input from a potentiometer to control the brightness of an LED. The line int sensorValue = analogRead(A1); reads the analog input from pin A1, representing a DJ slider or knob. The subsequent analogWrite(led, sensorValue/4); adjusts the brightness of an LED on pin 11 based on this input, creating a dynamic and interactive simulation of volume or fade control. This part of the code adds a tangible and intuitive user interface element to the mini DJ player simulation.
(I also refer to the slides from Professor!)