Author: Aaron
Daito Manabe
-
muscle(smiles): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YxdlYFCp5Ic
-
teeth led: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QsWc58zmBKI
-
11 play box projection: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=H_eAkJ_o-pk
-
dynamic vr display view dependent tracking: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=24&v=G7ZQ4KiX1JE
-
-
Nosaj Thing: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_woNBiIyOKI
-
Phosphere: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=El82ewNJdNs
P5js – Web Serial – Handshake
Gravity Wind Serial
Motors
Slide deck
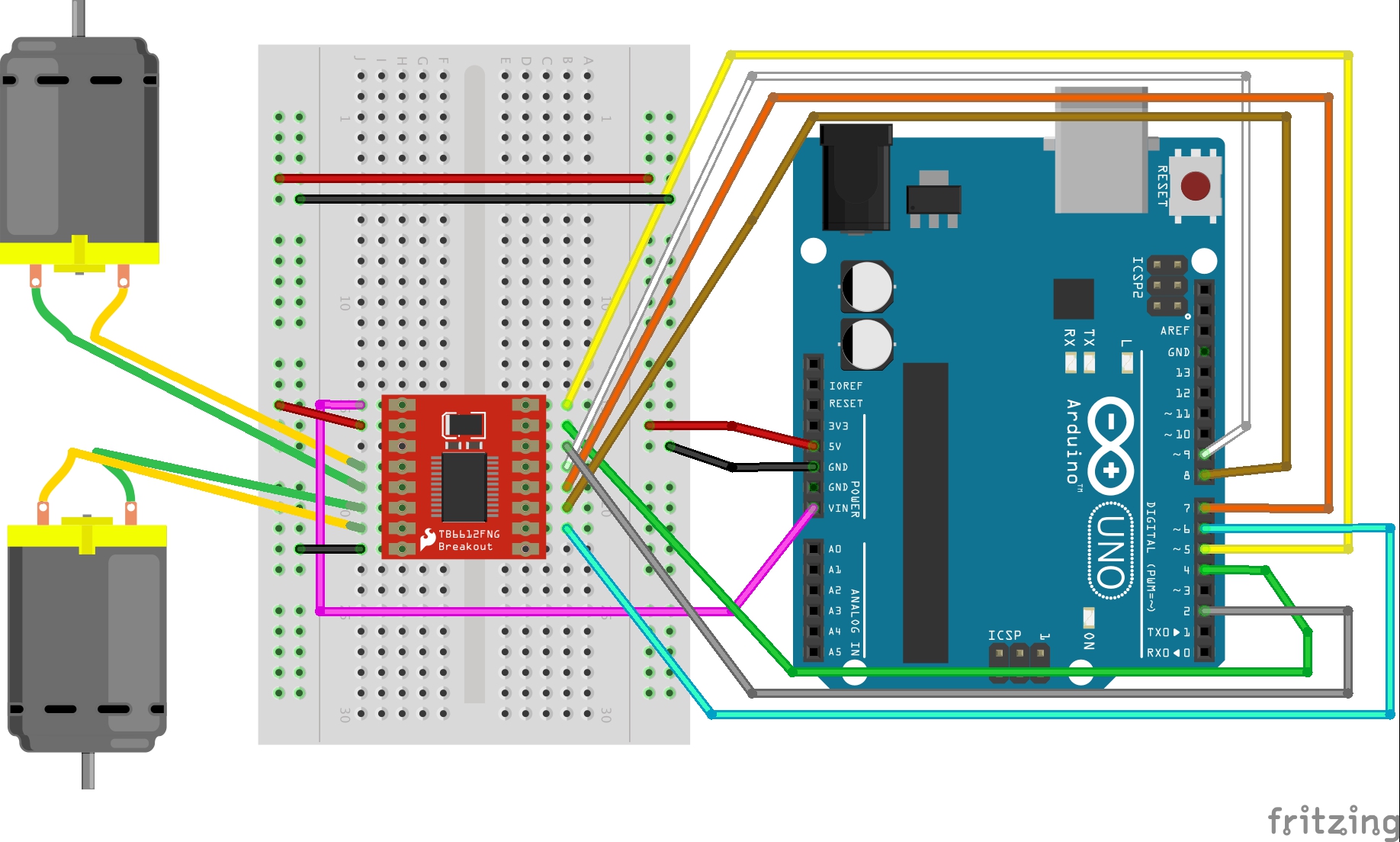
Motorshield
Link for Motor Shield tutorial: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/tb6612fng-hookup-guide?_ga=2.227433246.2072068385.1551701674-349683115.1523944725
Download the library here: TB6612FNG ARDUINO LIBRARY, or grab the latest version from Sparkfun’s GitHub repository. Once the library is installed, open the example code included in the Library through the Arduino IDE’s examples.
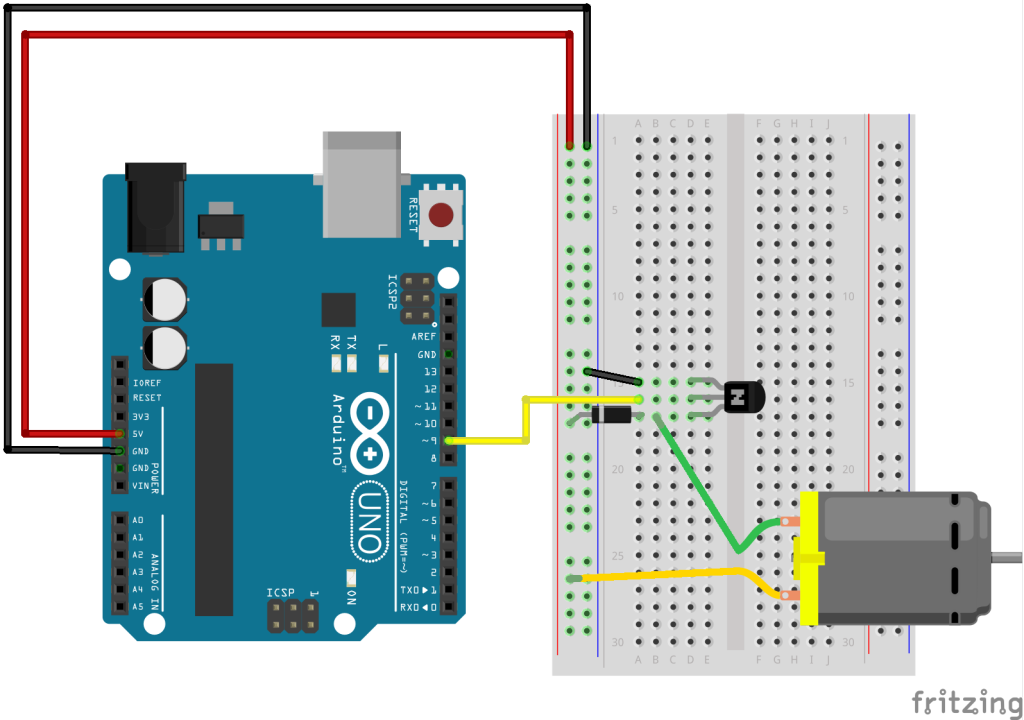
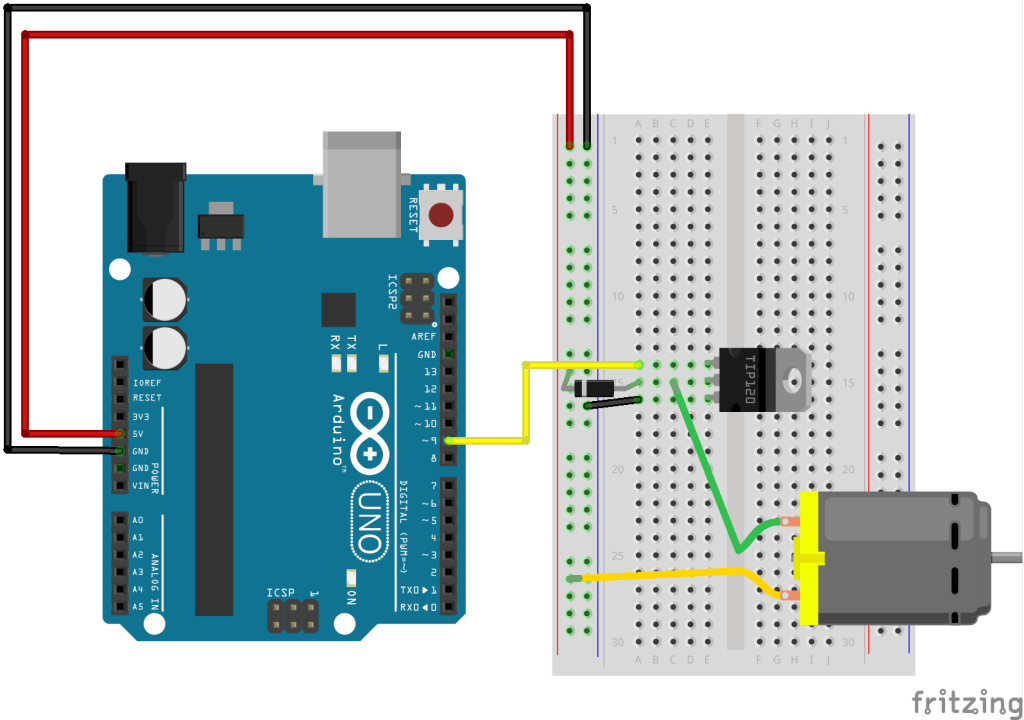
Transistor/diode
You would use the same set up with a diode and transistor for a solenoid as well.
With Smaller Transistor (P2N2222A or a BC337):
With Tip120:
Week 11 – Serial Communication – P5js
You will need the P5 Serial App: https://github.com/p5-serial/p5.serialcontrol/releases
Arduino Code:
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
while (Serial.available() <= 0) {
Serial.println("0,0"); // send a starting message
delay(300); // wait 1/3 second
}
}
void loop() {
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the incoming byte:
int inByte = Serial.read();
switch (inByte) {
case 0:
digitalWrite(2, LOW);
digitalWrite(5, LOW);
break;
case 1:
digitalWrite(2, HIGH);
break;
case 2:
digitalWrite(5, HIGH);
break;
}
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
Serial.print(sensorValue);
Serial.print(",");
sensorValue = analogRead(A1);
Serial.print(sensorValue);
Serial.println();
}
}
P5js – Editor Code
Exercises:
- make something that uses only one sensor on arduino and makes the ellipse in processing move on the horizontal axis, in the middle of the screen, and nothing on arduino is controlled by processing
-
make something that controls the LED brightness from processing
-
take the gravity wind example below and make it so every time the ball bounces one led lights up and then turns off, and you can control the wind from one analog sensor
Gravity Wind (press space bar for new ball drop)
More Resources: https://itp.nyu.edu/physcomp/labs/#Asynchronous_Serial
Musical Instrument Examples
- peter vogel https://vimeo.com/19780802
- field: jacks performance: https://vimeo.com/149364292
- giant instrument: https://vimeo.com/95706212
- nyc subway: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QjwxE_kI5wA
- interface example: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5B-0zGBwMx4
- me robospiel: https://vimeo.com/50586230
- servo drum machine: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EXgQfelajZc
- servo harp: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CtvZJb9VMkE
- block example: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0HobOt06gOI
- chordocentric: http://loisliow.netii.net/project2.html
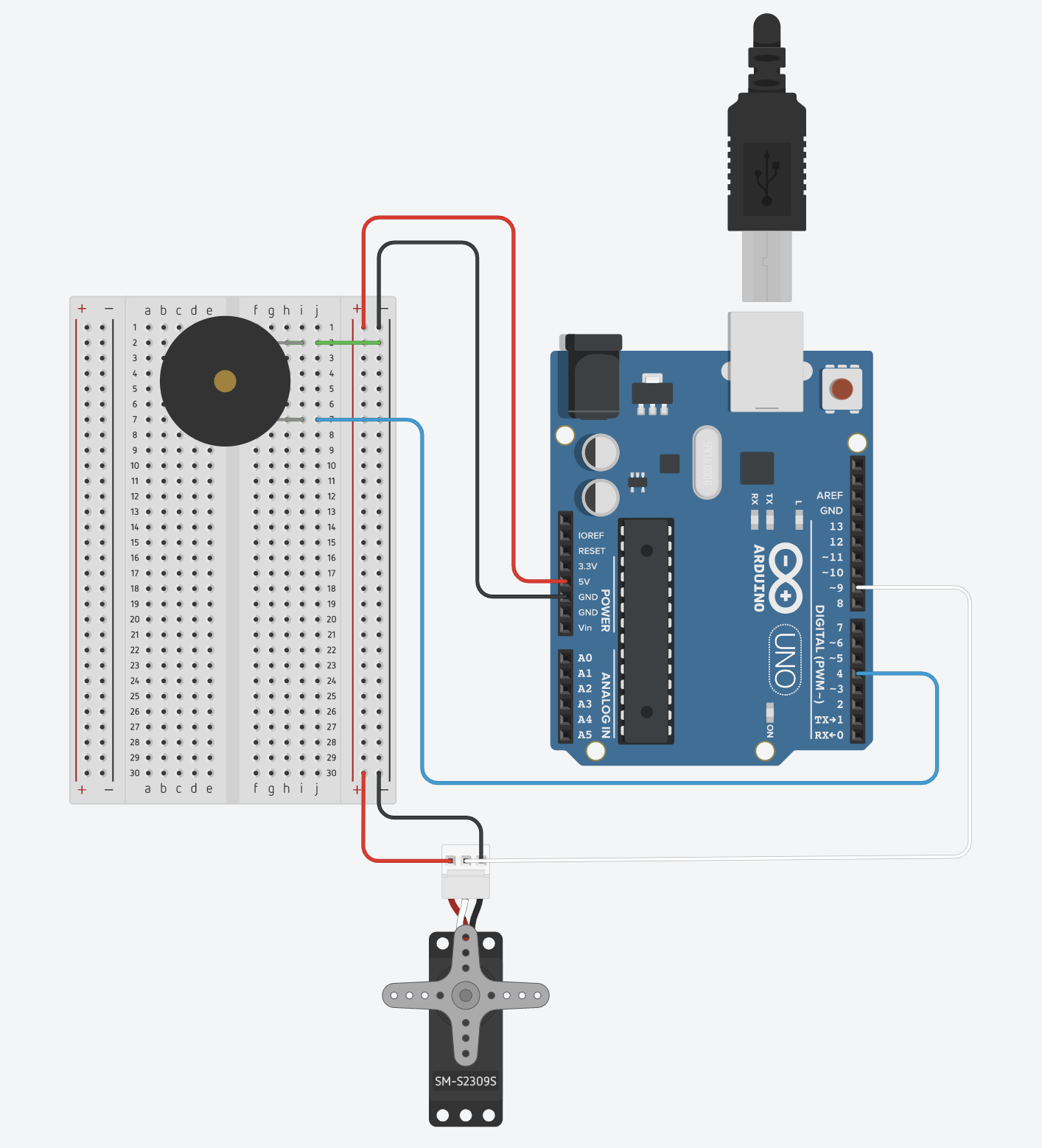
Week 10 – Servo and Tone
pitches.h:
/************************************************* * Public Constants *************************************************/ #define NOTE_B0 31 #define NOTE_C1 33 #define NOTE_CS1 35 #define NOTE_D1 37 #define NOTE_DS1 39 #define NOTE_E1 41 #define NOTE_F1 44 #define NOTE_FS1 46 #define NOTE_G1 49 #define NOTE_GS1 52 #define NOTE_A1 55 #define NOTE_AS1 58 #define NOTE_B1 62 #define NOTE_C2 65 #define NOTE_CS2 69 #define NOTE_D2 73 #define NOTE_DS2 78 #define NOTE_E2 82 #define NOTE_F2 87 #define NOTE_FS2 93 #define NOTE_G2 98 #define NOTE_GS2 104 #define NOTE_A2 110 #define NOTE_AS2 117 #define NOTE_B2 123 #define NOTE_C3 131 #define NOTE_CS3 139 #define NOTE_D3 147 #define NOTE_DS3 156 #define NOTE_E3 165 #define NOTE_F3 175 #define NOTE_FS3 185 #define NOTE_G3 196 #define NOTE_GS3 208 #define NOTE_A3 220 #define NOTE_AS3 233 #define NOTE_B3 247 #define NOTE_C4 262 #define NOTE_CS4 277 #define NOTE_D4 294 #define NOTE_DS4 311 #define NOTE_E4 330 #define NOTE_F4 349 #define NOTE_FS4 370 #define NOTE_G4 392 #define NOTE_GS4 415 #define NOTE_A4 440 #define NOTE_AS4 466 #define NOTE_B4 494 #define NOTE_C5 523 #define NOTE_CS5 554 #define NOTE_D5 587 #define NOTE_DS5 622 #define NOTE_E5 659 #define NOTE_F5 698 #define NOTE_FS5 740 #define NOTE_G5 784 #define NOTE_GS5 831 #define NOTE_A5 880 #define NOTE_AS5 932 #define NOTE_B5 988 #define NOTE_C6 1047 #define NOTE_CS6 1109 #define NOTE_D6 1175 #define NOTE_DS6 1245 #define NOTE_E6 1319 #define NOTE_F6 1397 #define NOTE_FS6 1480 #define NOTE_G6 1568 #define NOTE_GS6 1661 #define NOTE_A6 1760 #define NOTE_AS6 1865 #define NOTE_B6 1976 #define NOTE_C7 2093 #define NOTE_CS7 2217 #define NOTE_D7 2349 #define NOTE_DS7 2489 #define NOTE_E7 2637 #define NOTE_F7 2794 #define NOTE_FS7 2960 #define NOTE_G7 3136 #define NOTE_GS7 3322 #define NOTE_A7 3520 #define NOTE_AS7 3729 #define NOTE_B7 3951 #define NOTE_C8 4186 #define NOTE_CS8 4435 #define NOTE_D8 4699 #define NOTE_DS8 4978
#include <Servo.h>
#include "pitches.h"
Servo servo;
int servoPos = 100;
int whichNote = 0;
int notes[10] = {NOTE_C4, NOTE_D4, NOTE_E4, NOTE_F4, NOTE_G4, NOTE_A4, NOTE_B4, NOTE_C5, NOTE_D5, NOTE_E5};
int durations[10];
void setup() {
servo.attach(9);
pinMode(4, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
// set the durations with a random coinflip
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int coinFlip = random(2);
if (coinFlip == 0)
durations[i] = 8;
else
durations[i] = 4;
}
}
void loop() {
int val = analogRead(A0);
// the rate is 1 second divided by the duration of the note
int rate = 1000 / durations[whichNote];
// get the current time
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
// trigger a note
if (currentTime % rate == 0 ) {
tone(4, notes[whichNote], random(100, 400));
whichNote = random(10);
delay(1);
}
// do the servo at half speed
if (currentTime % (rate * 2) == 0 ) {
servoPos = 50;
servo.write(servoPos);
}
// else if not triggereing the servo, then every 10 milliseconds move the servo arm back a little bit
// can't do it every frame as that is too fast for the servo
else if (currentTime % 10 == 0) {
servoPos -= 1;
servo.write(servoPos);
}
}
- Timer0 – used for millis(), micros(), delay() and PWM on pins 5 & 6
- Timer1 – used for Servos, the WaveHC library and PWM on pins 9 & 10
- Timer2 – used by Tone and PWM on pins 3 & 11
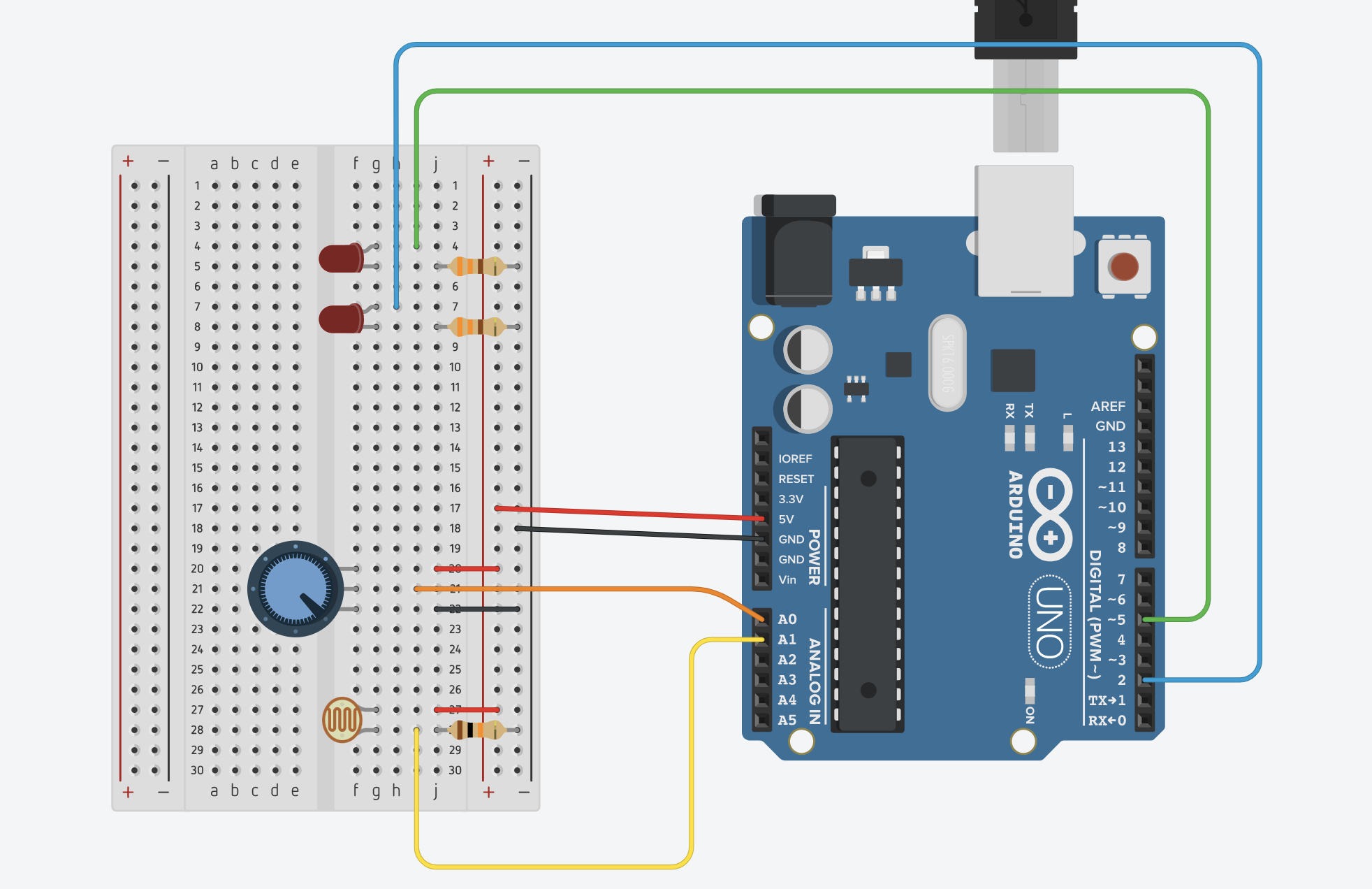
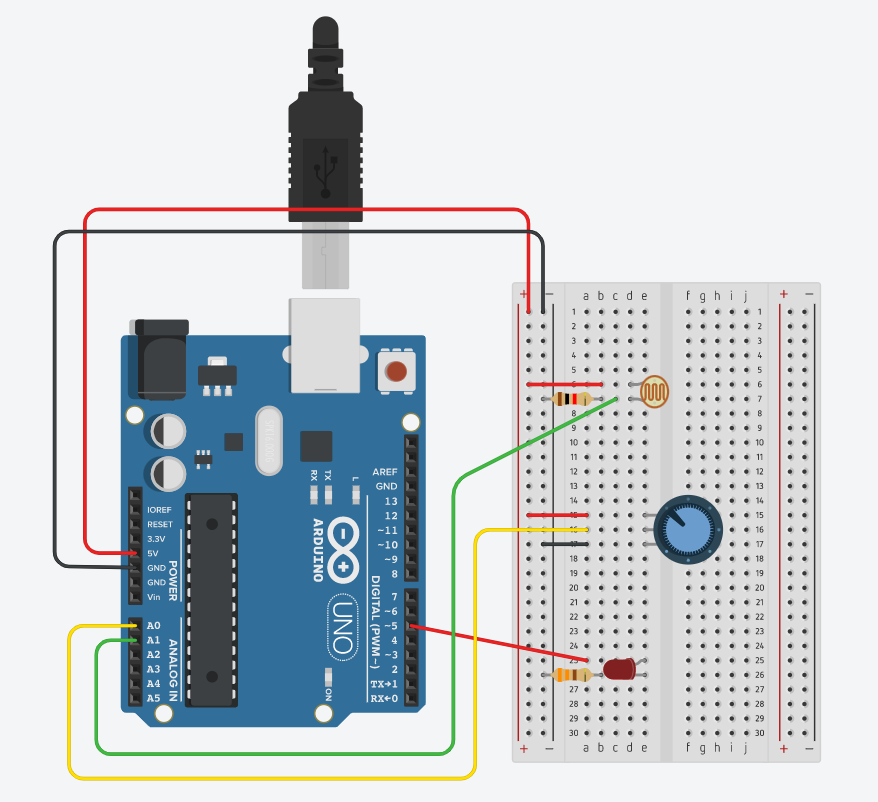
Week 9b – Analog Input & Output
// NOTE: to make a voltage divider for the photo resistor (which you need)
// use a 10k ohm resistor
void setup() {
// begin the serial connection at 9600 bits per second
// (the baud rate)
Serial.begin(9600);
// for analog output connect to any of the PWM pins
// these all have a tilda beside the pin number (~)
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// read the potentiometer on analog input pin A0
int potValue = analogRead(A0); // analog read gives values in a maximum range of 0-1023
// map the values from the potentiometer from 0-1023
// into the range of an analog write (0-255)
int mappedPotValue = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// read the photocell on analog input pin A1
int lightValue = analogRead(A1);
// print out the light value so we know the range
Serial.println(lightValue);
// based on the lowest and the highest numbers from the sensor,
// map those to the analogWrite range
// for example, if the lowest number is 500 nd the highest is 900
// then do:
int mappedLightValue = map(lightValue, 500, 900, 0, 255);
// sometimes the numbers might go lower or higher than 500 or 900
// it's important to constrain the mapped value
//to never go lower than 0 and never higher than 255
int constrainedValue = constrain(mappedLightValue, 0, 255);
// finally, take the number from the photocell, that was mapped,
// and then constrained, and use that for the call to analogWrite
analogWrite(5, constrainedValue);//0-255
}
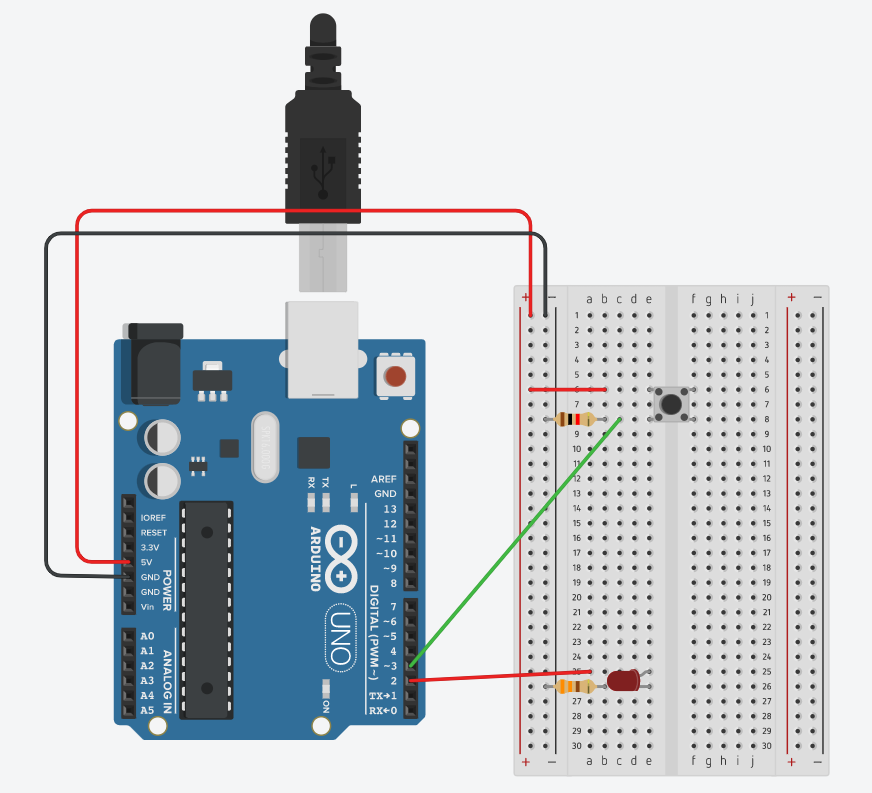
Week 9a Digital Input and Output
const int ledPin = 2;
const int buttonPin = 3;
unsigned long timer = 0;
bool onOff = LOW;
byte prevButtonState = LOW;
bool blinking = false;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// read the button pin
// store that in a local variable
byte buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
// print out the state of the button stored in the variable
Serial.println(buttonState);
// check to see if the button is pressed and last time it wasn't
// only do something if that is the case
if (buttonState == HIGH && prevButtonState == LOW) {
// change blinking to not blinking
blinking = !blinking;
}
// record the current button state for use next time through loop
prevButtonState = buttonState;
// if blinkkng is true, do the blinking stuff
if (blinking == true) {
// check to see if the current time (millis) is greater than the timer we recorded
if (millis() > timer) {
// flip the boolean
onOff = !onOff;
// record a new time to check against
timer = millis() + 250;
// turn the led on and off
digitalWrite(ledPin, onOff);
}
/ otherwise turn the LED off
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}