Exercise 1
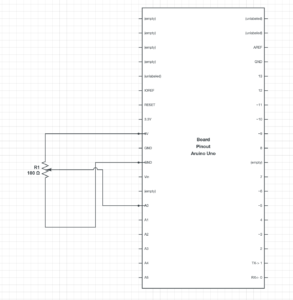
Using the potentiometer on arduino, I controlled the horizontal position of an ellipse in p5js.
Schematic:
The p5js sktech:
// variable to hold an instance of the p5.webserial library:
const serial = new p5.WebSerial();
// HTML button object:
let portButton;
let inData;
// for incoming serial data
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 300); // make the canvas
// check to see if serial is available:
if (!navigator.serial) {
alert("WebSerial is not supported in this browser. Try Chrome or MS Edge.");
}
// if serial is available, add connect/disconnect listeners:
navigator.serial.addEventListener("connect", portConnect);
navigator.serial.addEventListener("disconnect", portDisconnect);
// check for any ports that are available:
serial.getPorts();
// if there's no port chosen, choose one:
serial.on("noport", makePortButton);
// open whatever port is available:
serial.on("portavailable", openPort);
// handle serial errors:
serial.on("requesterror", portError);
// handle any incoming serial data:
serial.on("data", serialEvent);
serial.on("close", makePortButton);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
fill(255, 129, 200);
ellipse(inData, height/2, 40, 40);
}
// if there's no port selected,
// make a port select button appear:
function makePortButton() {
// create and position a port chooser button:
portButton = createButton("choose port");
portButton.position(10, 10);
// give the port button a mousepressed handler:
portButton.mousePressed(choosePort);
}
// make the port selector window appear:
function choosePort() {
if (portButton) portButton.show();
serial.requestPort();
}
// open the selected port, and make the port
// button invisible:
function openPort() {
// wait for the serial.open promise to return,
// then call the initiateSerial function
serial.open().then(initiateSerial);
// once the port opens, let the user know:
function initiateSerial() {
console.log("port open");
}
// hide the port button once a port is chosen:
if (portButton) portButton.hide();
}
// pop up an alert if there's a port error:
function portError(err) {
alert("Serial port error: " + err);
}
// read any incoming data as a string
// (assumes a newline at the end of it):
function serialEvent() {
inData = Number(serial.read());
console.log(inData);
}
// try to connect if a new serial port
// gets added (i.e. plugged in via USB):
function portConnect() {
console.log("port connected");
serial.getPorts();
}
// if a port is disconnected:
function portDisconnect() {
serial.close();
console.log("port disconnected");
}
function closePort() {
serial.close();
}
The arduino code:
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize serial communications
}
void loop() {
// read the input pin:
int potentiometer = analogRead(A0);
// remap the pot value to fit in 1 byte:
int mappedPot = map(potentiometer, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// print it out the serial port:
Serial.write(mappedPot);
// slight delay to stabilize the ADC:
delay(0.00001);
}
Video demo:
Exercise 2
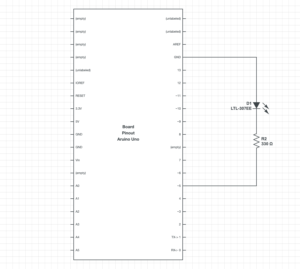
I utilized the mousedragged event in p5js to control the brightness of an LED. I mapped the mouseX position to a value between 0-255 and sent the value to the analogwrite function to control the brightness.
Schematic:
The arduino code:
int ledPin = 5;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize serial communications
}
void loop() {
if(Serial.available()) {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // led on while receiving data
int light = Serial.read();
Serial.println(light);
analogWrite(ledPin, light);
}
}
The p5js sketch:
let mpos = 0;
// variable to hold an instance of the p5.webserial library:
const serial = new p5.WebSerial();
// HTML button object:
let portButton;
let inData; // for incoming serial data
let outByte = 0; // for outgoing data
function setup() {
createCanvas(400, 300); // make the canvas
// check to see if serial is available:
if (!navigator.serial) {
alert("WebSerial is not supported in this browser. Try Chrome or MS Edge.");
}
// if serial is available, add connect/disconnect listeners:
navigator.serial.addEventListener("connect", portConnect);
navigator.serial.addEventListener("disconnect", portDisconnect);
// check for any ports that are available:
serial.getPorts();
// if there's no port chosen, choose one:
serial.on("noport", makePortButton);
// open whatever port is available:
serial.on("portavailable", openPort);
// handle serial errors:
serial.on("requesterror", portError);
// handle any incoming serial data:
//serial.on("data", serialEvent);
serial.on("close", makePortButton);
}
function draw() {
background(0);
fill(255);
text("Mouse position is: "+ mpos, 30, 50);
}
function mouseDragged() {
// map the mouseY to a range from 0 to 255:
mpos = int(map(mouseX, 0, width, 0, 255));
// send it out the serial port:
serial.write(mpos);
}
// if there's no port selected,
// make a port select button appear:
function makePortButton() {
// create and position a port chooser button:
portButton = createButton("choose port");
portButton.position(10, 10);
// give the port button a mousepressed handler:
portButton.mousePressed(choosePort);
}
// make the port selector window appear:
function choosePort() {
if (portButton) portButton.show();
serial.requestPort();
}
// open the selected port, and make the port
// button invisible:
function openPort() {
// wait for the serial.open promise to return,
// then call the initiateSerial function
serial.open().then(initiateSerial);
// once the port opens, let the user know:
function initiateSerial() {
console.log("port open");
}
// hide the port button once a port is chosen:
if (portButton) portButton.hide();
}
// pop up an alert if there's a port error:
function portError(err) {
alert("Serial port error: " + err);
}
// try to connect if a new serial port
// gets added (i.e. plugged in via USB):
function portConnect() {
console.log("port connected");
serial.getPorts();
}
// if a port is disconnected:
function portDisconnect() {
serial.close();
console.log("port disconnected");
}
function closePort() {
serial.close();
}
Video demo:
Exercise 3
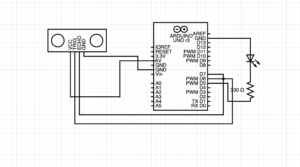
I used the ultrasonic sensor on the arduino as an anolog sensor to control the wind in the gravity wind sketch. I also created a variable which changes value between 1 and 0 whenever the ball bounced and sent the data over to arduino.
The arduino code:
#include <NewPing.h>
int ledPin = 5;
const int trig_v = 6;
const int echo_v = 7;
int max_d = 45;
int light;
NewPing dist(trig_v, echo_v, max_d);
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize serial communications
}
void loop() {
int wind = dist.ping_cm();
//Serial.print("wind = ");
Serial.println(wind);
delay(1);
light = Serial.parseInt();
digitalWrite(ledPin, light);
//delay(1);
}
The p5js sketch:
let velocity;
let gravity;
let position;
let acceleration;
let wind;
let wmap;
let drag = 0.99;
let mass = 50;
let bounce = 0;
function setup() {
createCanvas(640, 360);
noFill();
position = createVector(width/2, 0);
velocity = createVector(0,0);
acceleration = createVector(0,0);
gravity = createVector(0, 0.5*mass);
wind = createVector(0,0);
}
function draw() {
background(255);
wind = createVector(wmap, 0);
if (!serialActive) {
fill(0);
text("Click the mouse to select Serial Port", 20, 30);
} else {
text("Connected", 20, 30)
applyForce(wind);
applyForce(gravity);
velocity.add(acceleration);
velocity.mult(drag);
position.add(velocity);
acceleration.mult(0);
ellipse(position.x,position.y,mass,mass);
if(position.x > width){
position.x = 0;
}
if(position.y > height-mass/2){
if(bounce == 0){
bounce = 1;
}else{
bounce = 0;
}
}
if (position.y > height-mass/2) {
velocity.y *= -1.25; // A little dampening when hitting the bottom
position.y = height-mass/2;
}
}
}
function applyForce(force){
// Newton's 2nd law: F = M * A
// or A = F / M
let f = p5.Vector.div(force, mass);
acceleration.add(f);
}
function keyPressed(){
if (keyCode==LEFT_ARROW){
wind.x=-1;
}
if (keyCode==RIGHT_ARROW){
wind.x=1;
}
if (key==' '){
mass=random(15,80);
position.y=-mass;
velocity.mult(0);
}
}
function mouseClicked()
{
setUpSerial();
}
function readSerial(data) {
if (data != null) {
wmap = int(data);
console.log(wmap);
}
//////////////////////////////////
//SEND TO ARDUINO HERE (handshake)
//////////////////////////////////
let sendToArduino = bounce;
console.log("bounce "+bounce);
writeSerial(sendToArduino);
}
Video demo: