const int knobPin = A0;
const int ledPin = 3; // be sure to use a PWM pin!
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// read the potentiometer value
int knobValue = analogRead(knobPin);
// analog write takes values between 0 and 255
// map the knob value to be be between 0 and 255
int brightness = map(knobValue,0,1023,0,255);
// use the brightness value for the LED analog write
analogWrite(ledPin, brightness);
}
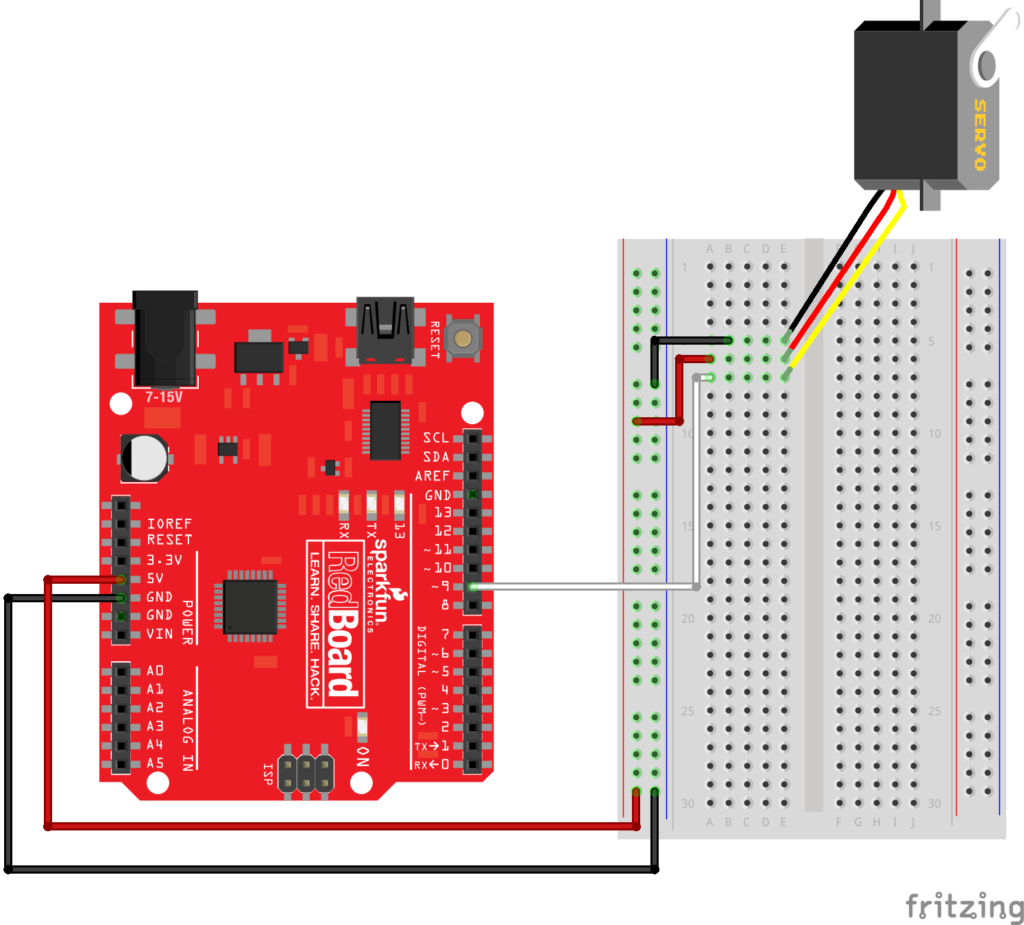
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myServo;
const int knobPin = A0;
void setup() {
// attach the servo to pin number 9
myServo.attach(9);
}
void loop() {
// read the potentiometer value
int knobValue = analogRead(knobPin);
// the servo only moves between 0 and 180
// map the knob value to be be between 0 and 180
int angle = map(knobValue,0,1023,0,180);
// use the mapped angle to set the servo's rotation
myServo.write(angle);
// wait a very short bit for the servo to move to the location
delay(15);
}
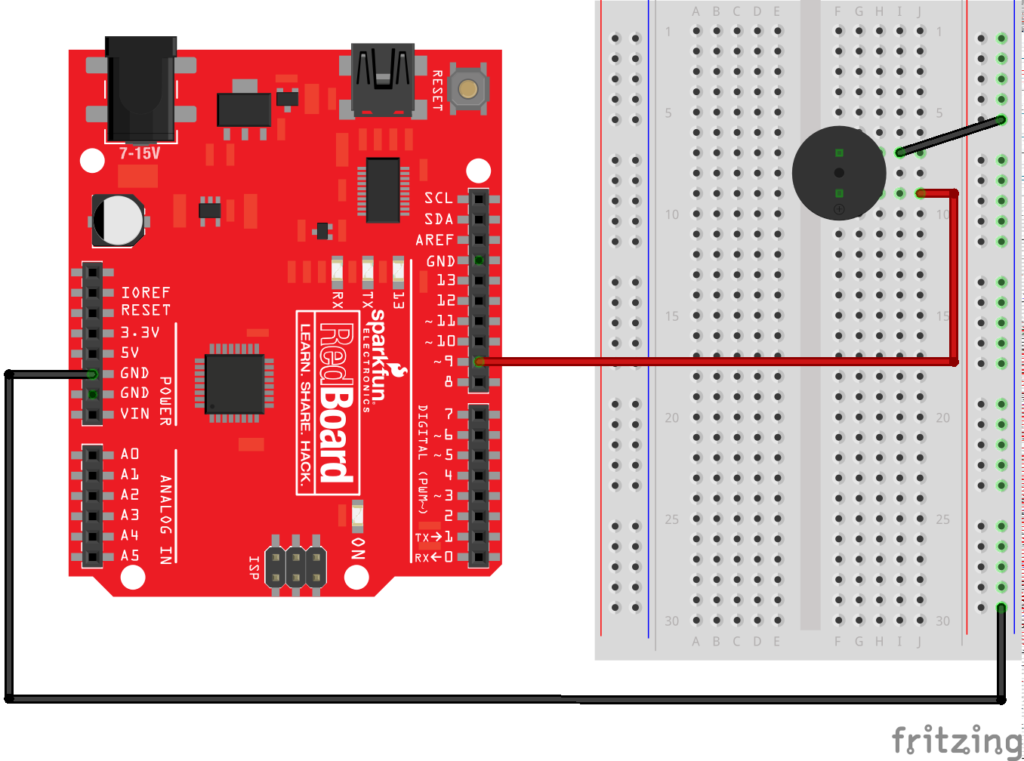
int buzzerPin = 4;
void setup() {
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// arguments are pin, frequency, and duration
tone(buzzerPin, 440, 200);
// since the tone is lasting 200 milliseconds
// delay for 400, so 200 on and then 200 off
delay(400);
// you could also do without the duration argument if you wanted a steady tone:
// tone(buzzerPin, 440);
}
Install the Tone Library by Brett Hagman to use more than one Buzzer:
// install the Tone Library by Brett Hagman to use multiple buzzers
#include <Tone.h>
// arrays to hold the note values
int notes[10] = {NOTE_C4, NOTE_D4, NOTE_E4, NOTE_F4, NOTE_G4, NOTE_A4, NOTE_B4, NOTE_C5, NOTE_D5, NOTE_E5};
Tone player0, player1;
// length in milliseconds
int duration = 250;
//variable to change note for player0
int whichNote = 0;
void setup() {
// use pin 5 for buzzer 0
player0.begin(5);
// use pin 6 for buzzer 1
player1.begin(6);
}
void loop() {
// player0's notes change according to the number in whichNote
player0.play(notes[whichNote], duration);
// player1's note stays the same
player1.play(notes[9], duration);
// set whichNote to equal itself + 1
// then modulo that number by 8, which creates a loop between 0-7 (8 digits)
whichNote = (whichNote + 1) % 8; //do plus 1 to go up major scale, try others numbers like plus 3
//wait for the notes to stop playing before going to the next note
delay(duration);
}