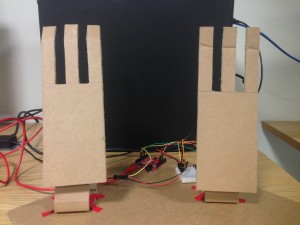
For this week’s assignment, I made two hands that may or may not shake each other, depending on the degree of excitement.
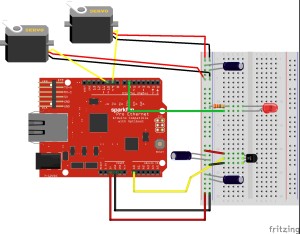
I used two servos to control the left and right hand, respectively. Once the device is connected to power, the left hand will move first, meaning the left hand wants to meet a new hand. Then the right hand will move to meet the left hand. At this stage, two things can happen: either the two hands will start shaking or they will return to the default position. In other words, if the left hand feels that the right hand is excited to meet him, they will shake each other. Otherwise, the hands will return to the default position, because the left hand is not satisfied with the degree of excitement. In my circuit, the degree of excitement is measured by a temperature sensor. Higher temperatures imply higher degrees of excitement. The red LED will light up if the left hand is satisfied with the degree of excitement.
One problem I encountered is the fluctuating reading values on my temperature sensor. To solve this problem, Scott suggests that I use the code for smoothing, which works perfectly to bring the reading back to normal state.
The video below shows how my device works. The code for my program is attached after the video.
#include <Servo.h>
Servo servoLeft; // Define left servo
Servo servoRight; // Define right servo
//set variables
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int x = 130;
int y = 50;
//smoothing
const int numReadings = 10;
int readings[numReadings]; // the readings from the analog input
int readIndex = 0; // the index of the current reading
int total = 0; // the running total
int average = 0; // the average (this will be the value you use in your sketch)
int inputPin = A0;
void setup()
{
servoLeft.attach(10); // Set left servo to digital pin 10
servoRight.attach(9); // Set right servo to digital pin 9
pinMode(6, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
//set the hands to default positions
servoLeft.write(0);
servoRight.write(180);
delay(2000);
//smoothing
for (int thisReading = 0; thisReading < numReadings; thisReading++) {
readings[thisReading] = 0;
}
}
void loop() {
//smoothing
// set total var to 0
total = 0;
// read the sensor 10 times and add up the results
for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++) {
readings[x] = analogRead(inputPin); // store value in an array
total = total + readings[x]; // add the readings to the total
delay(2); // let the ADC settle
}
// calculate the average of the 10 readings:
average = total / 10;
// send it to the computer as ASCII digits
Serial.println(average);
//light up LED if excited
if (average > 145) {
digitalWrite(6, HIGH);
}else{
digitalWrite(6,LOW);
}
//move hand 1
if (a == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < 135; i += 5) {
servoLeft.write(i);
delay(100);
if (i == 130) {
a = 1; //break the loop when hand 1 reaches 150 degrees
}
}
}
// move hand 2
if (b == 0) {
for (int j = 180; j > 45; j -= 5) {
servoRight.write(j);
delay(100);
if (j == 50) {
b = 1;
}
}
}
//start shaking hands
if (average > 145) {
while ( x > 50 && y < 130) {
servoLeft.write(x);
x -= 10;
delay(50);
servoRight.write(y);
y += 10;
delay(50);
}
while (x < 130 && y > 50) {
servoLeft.write(x);
x += 10;
delay(50);
servoRight.write(y);
y -= 10;
delay(50);
}
while ( x > 50 && y < 130) {
servoLeft.write(x);
x -= 10;
delay(50);
servoRight.write(y);
y += 10;
delay(50);
}
while (x < 130 && y > 50) {
servoLeft.write(x);
x += 10;
delay(50);
servoRight.write(y);
y -= 10;
delay(50);
}
} else {
//set the hands to default positions
servoLeft.write(0);
servoRight.write(180);
delay(2000);
//reset the variables
a = 0;
b = 0;
delay(1000);
}
}