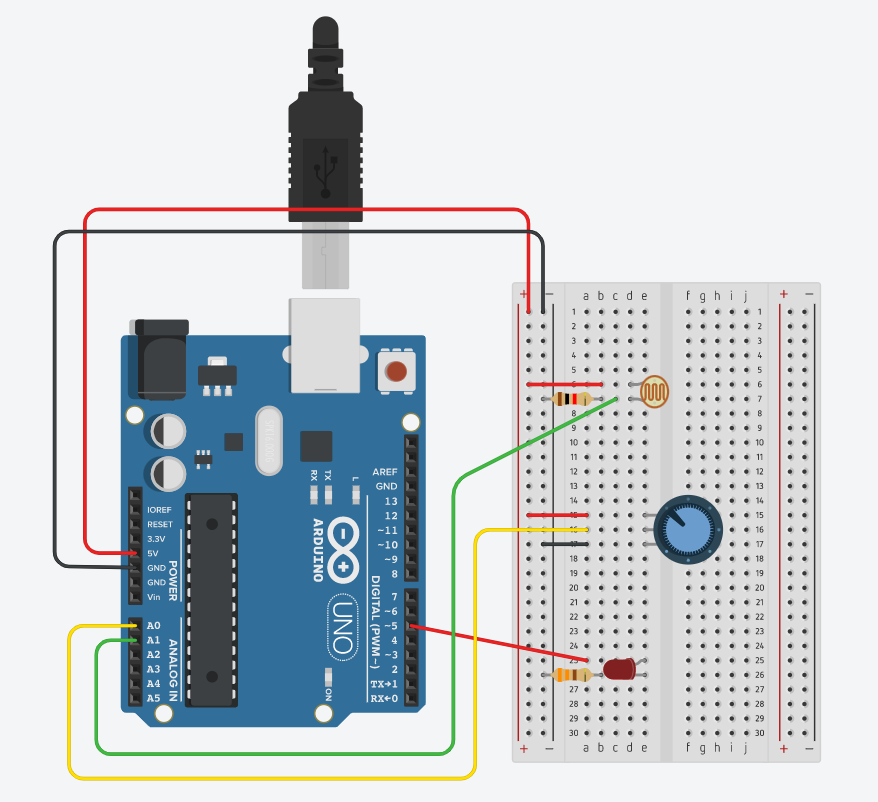
// NOTE: to make a voltage divider for the photo resistor (which you need)
// use a 10k ohm resistor
void setup() {
// begin the serial connection at 9600 bits per second
// (the baud rate)
Serial.begin(9600);
// for analog output connect to any of the PWM pins
// these all have a tilda beside the pin number (~)
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// read the potentiometer on analog input pin A0
int potValue = analogRead(A0); // analog read gives values in a maximum range of 0-1023
// map the values from the potentiometer from 0-1023
// into the range of an analog write (0-255)
int mappedPotValue = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
// read the photocell on analog input pin A1
int lightValue = analogRead(A1);
// print out the light value so we know the range
Serial.println(lightValue);
// based on the lowest and the highest numbers from the sensor,
// map those to the analogWrite range
// for example, if the lowest number is 500 nd the highest is 900
// then do:
int mappedLightValue = map(lightValue, 500, 900, 0, 255);
// sometimes the numbers might go lower or higher than 500 or 900
// it's important to constrain the mapped value
//to never go lower than 0 and never higher than 255
int constrainedValue = constrain(mappedLightValue, 0, 255);
// finally, take the number from the photocell, that was mapped,
// and then constrained, and use that for the call to analogWrite
analogWrite(5, constrainedValue);//0-255
}

