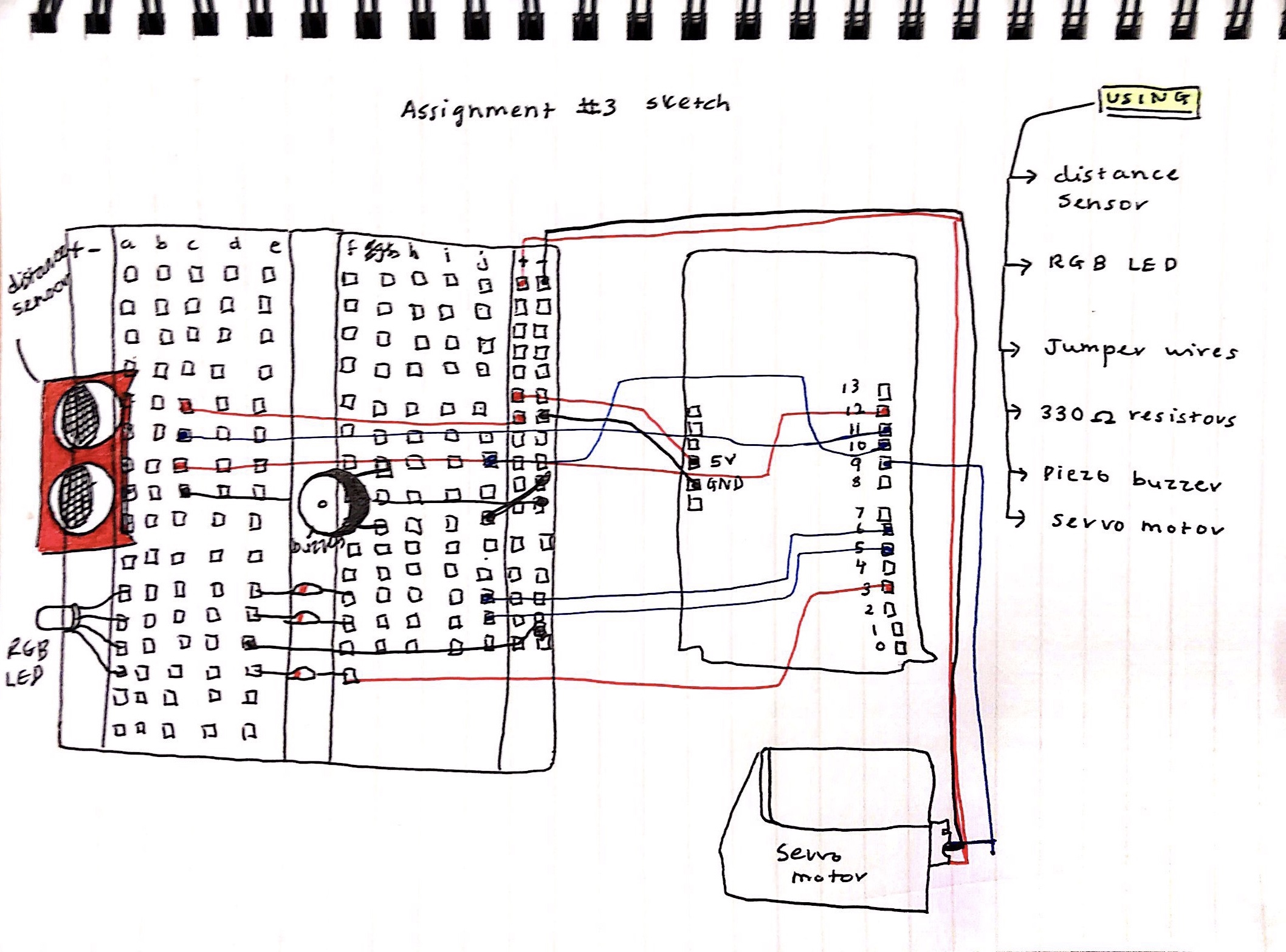
For this assignment, we were asked to control an LED in an “unexpected” way using information from an analog sensor. Going off of this prompt, I created a ‘Safeguard’ using a motion sensor, a servo motor, a buzzer, and an RGB LED light. Here is a rough circuit sketch:
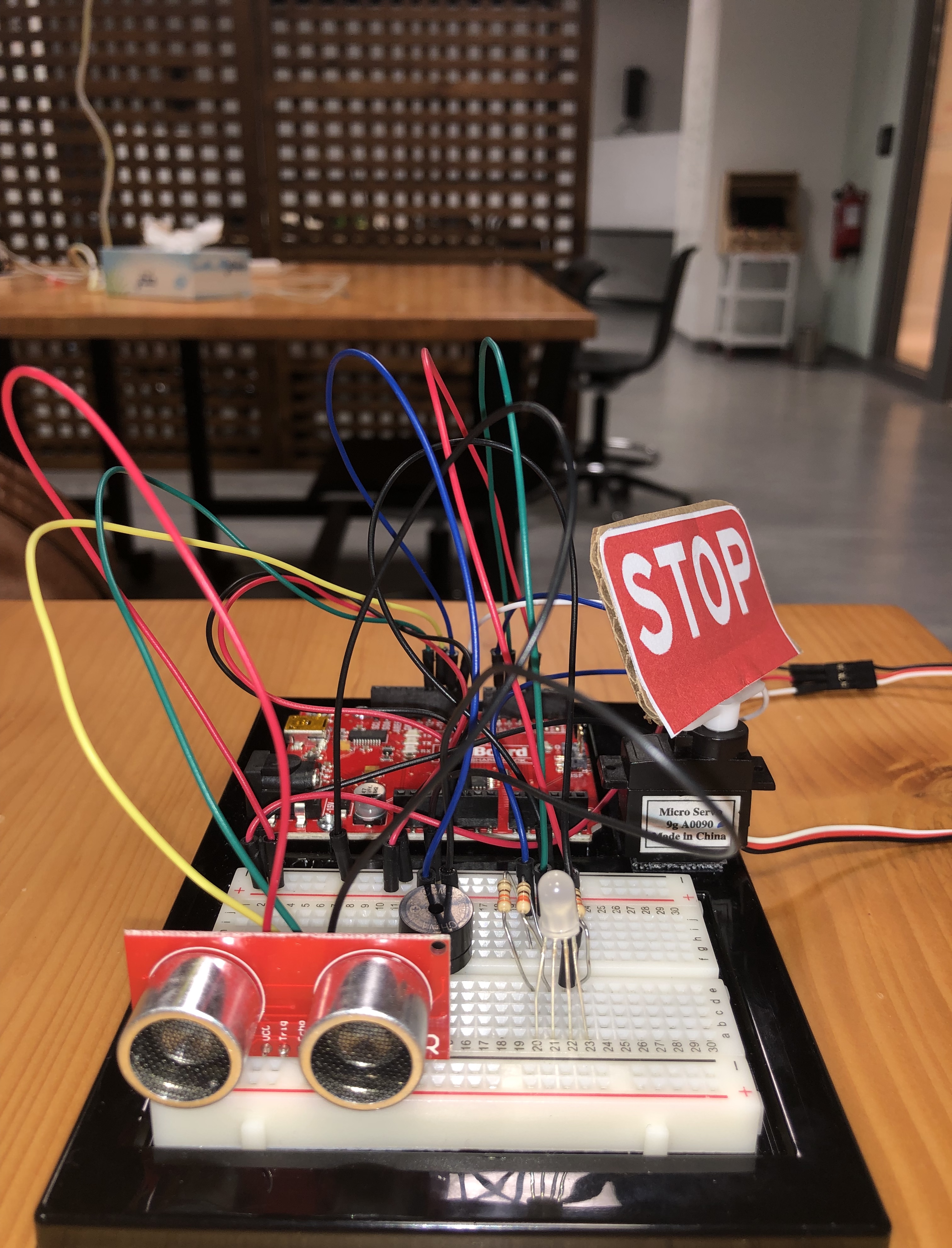
The LED lights up based on readings from the motion sensor about the object’s proximity; so if the object or person is at a safe distance, the LED turns green. At a medium distance, it turns yellow. When the object gets too close to the sensor, the LED turns red and triggers sound from the buzzer along with a movement from the servo motor. Although the stop sign kind of hints at the outcome, there is a sense of ‘surprise’ in that you don’t know how or when it is triggered unless you interact with the sensor. Here is an image of the circuit:
One of the challenges I faced while making this was that I wanted the stop sign to be part of the circuit, rather than a mere cardboard cutout. However, I realized that using a servo to move the sign around reconciles that. If I were to improve this project, I would incorporate an LCD screen to use instead of the cardboard sign.
Here is a final video demonstration:
And here, you can find the code I used to make it work:
#include <Servo.h>
const int trigPin = 11;
const int echoPin = 12;
const int redPin = 3;
const int greenPin = 5;
const int bluePin = 6;
const int buzzerPin = 10;
float distance = 0;
Servo myservo;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin (9600);
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
//set the RGB LED pins to output
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT);
myservo.attach(9);
}
void loop() {
distance = getDistance();
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" in");
if(distance <= 10){ //close distance
//make the RGB LED red
analogWrite(redPin, 255);
analogWrite(greenPin, 0);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
//this code moves the servo and triggers the buzzer
tone(buzzerPin, 272); //turn buzzer on
myservo.write(60); //move servo to 45 degrees
delay(100);
noTone(buzzerPin); //turn buzzer off
myservo.write(150); //move servo to 135 degrees
delay(100);
} else if(10 < distance && distance < 20){ //medium distance
//make the RGB LED yellow
analogWrite(redPin, 255);
analogWrite(greenPin, 50);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
} else{ //far distance
//make the RGB LED green
analogWrite(redPin, 0);
analogWrite(greenPin, 255);
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
}
delay(50); //delay 50ms between each reading
}
float getDistance()
{
float echoTime;
float calculatedDistance;
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
echoTime = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
calculatedDistance = echoTime / 148.0;
return calculatedDistance;
}
//credits: SparkFun Electronics.